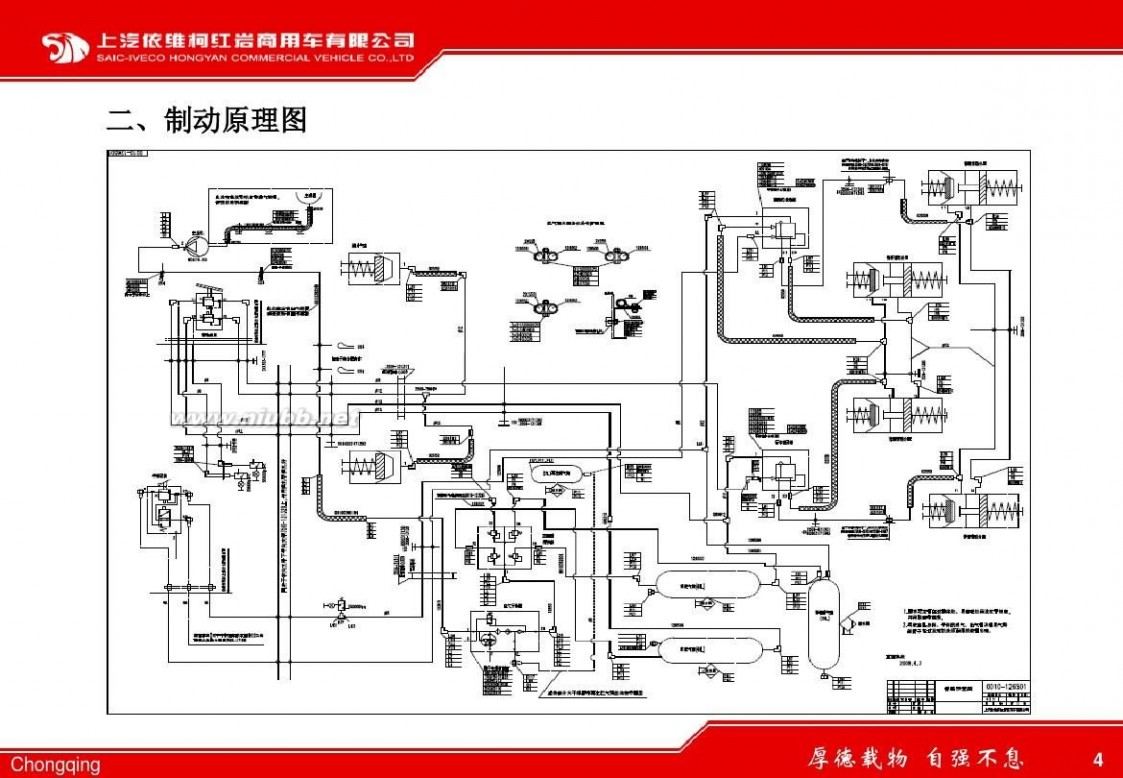
一 : 汽车制动系统组成和原理
制动系统(10)汽车(491)汽车制动系统组成和原理
组成
(1)供能装置:包括供给、调节制动所需能量以及改善传动介质状态的各种部件
(2)控制装置:产生制动动作和控制制动效果各种部件,如制动踏板
(3)传动装置:包括将制动能量传输到制动器的各个部件如制动主缸、轮缸
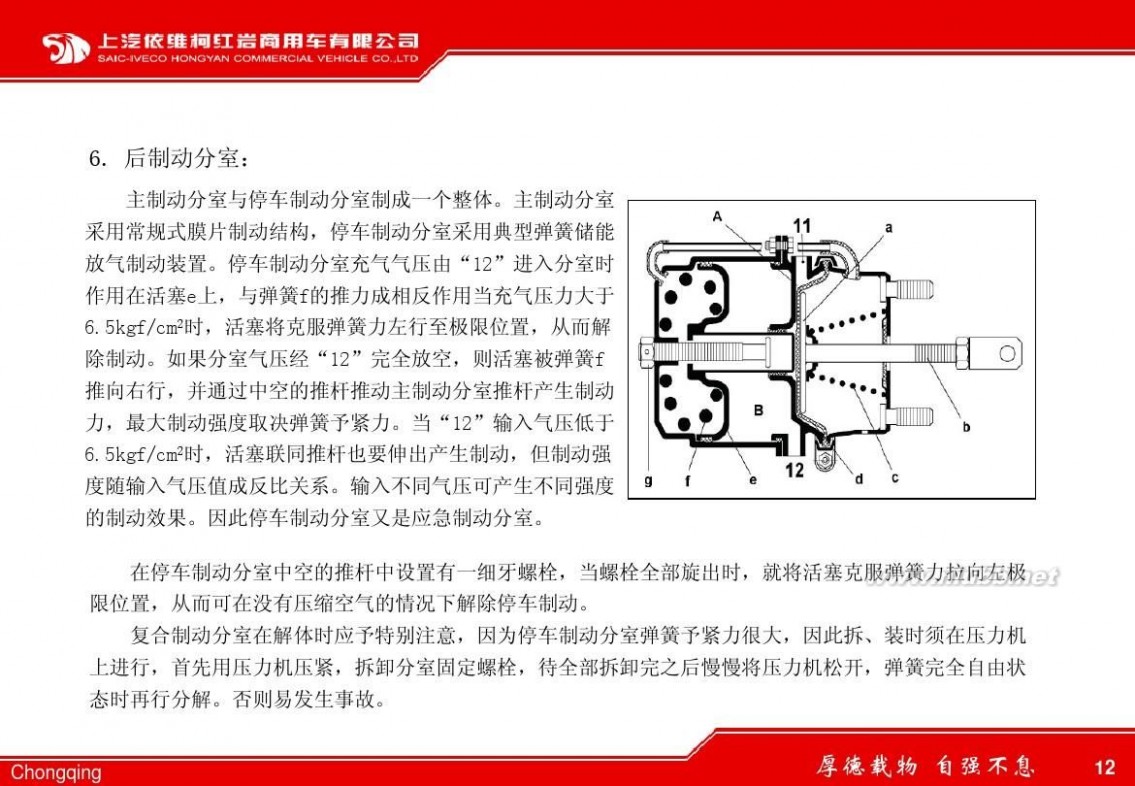
(4)制动器:产生阻碍车辆运动或运动趋势的部件
制动系统一般由制动操纵机构和制动器两个主要部分组成。
(1)制动操纵机构
产生制动动作、控制制动效果并将制动能量传输到制动器的各个部件,如图中的2、3、4、6,以及制动轮缸和制动管路。
(2)制动器
产生阻碍车辆的运动或运动趋势的力(制动力)的部件。汽车上常用的制动器都是利用固定元件与旋转元件工作表面的摩擦而产生制动力矩,称为摩擦制动器。它有鼓式制动器和盘式制动器两种结构型式。
原理
1、一般制动系的基本结构
·主要由车轮制动器和液压传动机构组成。
·车轮制动器主要由旋转部分、固定部分和调整机构组成,旋转部分是制动鼓;固定部分包括制动蹄和制动底板;调整机构由偏心支承销和调整凸轮组成用于调整蹄鼓间隙。
·制动传动机构主要由制动踏板、推杆、制动主缸、制动轮缸和管路组成。
2、制动工作原理
制动系统的一般工作原理是,利用与车身(或车架)相连的非旋转元件和与车轮(或传动轴)相连的旋转元件之间的相互摩擦来阻止车轮的转动或转动的趋势。
1)制动系不工作时
·蹄鼓间有间隙,车轮和制动鼓可自由旋转
2)制动时
·要汽车减速,脚踏下制动器踏板通过推杆和主缸活塞,使主缸油液在一定压力下流入轮缸,并通过两轮缸活塞推使制动蹄绕支承销转动,上端向两边分开而以其摩擦片压紧在制动鼓的内圆面上。不转的制动蹄对旋转制动鼓产生摩擦力矩,从而产生制动力
3)解除制动
·当放开制动踏板时回位弹簧即将制动蹄拉回原位,制动力消失。
3、制动主缸的结构及工作过程
·制动主缸的作用是将自外界输入的机械能转换成液压能,从而液压能通过管路再输给制动轮缸
·制动主缸分单腔和双腔式两种,分别用于单、双回路液压制动系。
(1)单腔式制动主缸
1)制动系不工作时
·不制动时,主缸活塞位于补偿孔、回油孔之间
2)制动时
·活塞左移,油压升高,进而车轮制动
3)解除制动
·撤除踏板力,回位弹簧作用,活塞回位,油液回流,制动解除
(2)双腔式制动主缸
1)结构(如一汽奥迪100型轿车双回路液压制动系统中的串联式双腔制动主缸)
·主缸有两腔
·第一腔与右前、左后制动器相连;第二腔与左前、右后制动器相通
·每套管路和工作腔又分别通过补偿孔和回油孔与储油罐相通。第二活塞由右端弹簧保持在正确的初始位置,使补偿孔和进油孔与缸内相通。第一活塞在左端弹簧作用下,压靠在套上,使其处于补偿孔和回油孔之间的位置。
2)工作原理
·制动时,第一活塞左移,油压升高,克服弹力将制动液送入右前左后制动回路;同时又推动第二活塞,使第二腔液压升高,进而两轮制动
·解除制动时,活塞在弹簧作用下回位,液压油自轮缸和管路中流回制动主缸。如活塞回位迅速,工作腔内容积也迅速扩大,使油压迅速降低。储液罐里的油液可经进油孔和活塞上面的小孔推开密封圈流入工作腔。当活塞完全回位时,补偿孔打开,工作腔内多余的油由补偿孔流回储液罐。若液压系统由于漏油,以及由于温度变化引起主缸工作腔、管路、轮缸中油液的膨胀或收缩,都可以通过补偿孔进行调节。
4、制动轮缸的结构及工作过程
·制动轮缸的功用:是将液力转变为机械推力。有单活塞和双活塞两种。
1)结构
·奥迪100的双活塞式轮缸体内有两活塞,两皮碗,弹簧使皮碗、活塞、制动蹄紧密接触。
2)工作过程
·制动时,液压油进入两活塞间油腔,进而推动制动蹄张开,实现制动。
·轮缸缸体上有放气螺栓,以保证制动灵敏可靠。
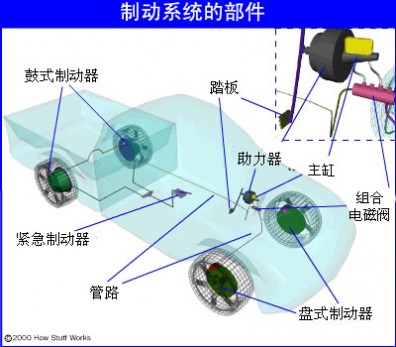 典型的制动系统 |
本文是制动系统六个部分的第一部分,我们将按踏板到车轮的顺序,从头到尾详细讲述制动系统的各个部分。本文将介绍汽车制动系统的基本概念,并分析一个简单制动系统的工作原理。在其他文章中,我们将向您介绍汽车制动系统的其他部件,并详细讲述每个部件的工作原理。
| 关于制动系统的其他文章主缸和组合阀工作原理鼓式制动器工作原理盘式制动器工作原理动力制动系统工作原理防抱死制动系统工作原理 |
您踩下制动踏板以后,汽车通过制动液将您的脚下发出的力传递到制动器。而制动实际上需要的力要远远大于您的脚所施加的力,因此汽车必须将您的脚施加的力放大。放大的方式有两种:
机械效益(杠杆作用)液压放大制动器通过摩擦将制动力传递到轮胎,轮胎则通过摩擦将制动力传递到路面。在开始讨论制动系统的各部件之前,先让我们熟悉一下以下三条原理:
杠杆作用液压作用摩擦力作用杠杆作用
制动踏板以如下方式设计,它可以将您腿部发出的力在传递到制动液之前就放大几倍。
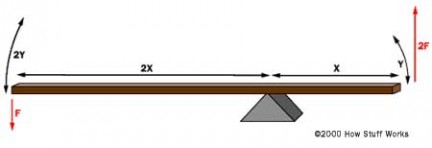 |
如上图所示,在杠杆的左端施加一个力F。杠杆左端的长度(2x)是右端(x)的两倍。因此,我们可以在杠杆右端获得一个2F的力,它运动的位移(y)则只是左端位移(2y)的一半。改变杠杆左右两端的相对长度,也就改变了放大系数。
液压系统
任何液压系统的基本原理都很简单:作用于某一点的力被不能压缩的液体传递到另一点,这种液体通常是油类液体。 绝大多数制动系统都是通过这一过程放大制动力的。下面是一个最简单的液压系统:
如上图所示:两个活塞(红色)分别装在充满油(蓝色)的两个玻璃圆桶中,圆桶之间由一个充满油的导管连接。如果给一个活塞(图中左边的活塞)施加一个向下的力,那么这个力就可以通过管道内的液压油传递到另一个活塞。由于油不能被压缩,所以这种传递方式的效率非常高,几乎所有的力都传递给了第二个活塞。液压系统最大的好处就是,连接两个液压缸的导管可以是任何长度,也可以曲折成各种形状以绕过中间的其他部件。此外,还有一个好处就是液压管可以分支,这样一个主缸就可以被分成多个副缸,如下图所示:
使用液压系统的另一个好处就是力的放大或缩小相当容易。如果您读过滑轮组的工作原理或齿轮比原理,您就会知道,用力换取位移在机械系统中极为常见。在液压系统中,您要做的就是改变其中一个活塞及其配套液压缸的尺寸,如下图所示:
上图中,力的放大倍数取决于活塞的直径。假设左边的活塞直径为5厘米,即半径为2.5厘米;右边的活塞直径为15厘米,即半径为7.5厘米。两个活塞的面积可以通过公式A=2πr2计算得出。左边活塞的面积为19.6平方厘米,右边活塞的面积为176平方厘米。右边活塞的面积是左边活塞的九倍。这就意味着给左边的活塞施加任何一个力,右边的活塞就会产生一个九倍的力。因此,如果给左边的活塞施加一个100公斤的向下的力,右边的活塞就会产生一个900公斤的向上的力。 唯一的不足就是当左边的活塞向下移动9厘米时,右边的活塞只能向上移动1厘米。
摩擦力
摩擦力是一个物体在另一个物体上滑动时受到的阻力。请看下图,两个滑块都是用相同材料做成的,但其中一个较另一个更重。所以不难看出哪一个更难推动。
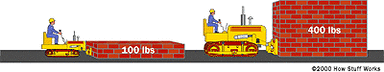 摩擦力与重量 |
我们可以通过近距离地观察其中一个滑块和桌面来了解其中的原因:
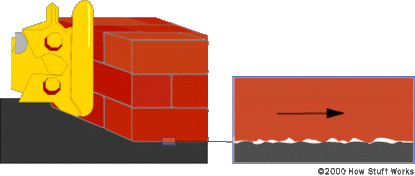 通过显微镜来研究摩擦力 |
用肉眼看起来很平滑的接触面,在显微镜下观察却是相当粗糙的。把滑块平放在桌面上时,滑块和桌面之间有许多小锯齿挤在一起,其中一些会相互咬合。滑块重量越大,咬合的锯齿就越多,其滑动阻力也会越大。
不同的材料具有不同的微观结构。例如,橡胶与橡胶之间就比钢铁与钢铁之间更难滑动。材料的类型决定了摩擦系数,此系数等于推动滑块所需的作用力与滑块重量的比值。在上例中,如果摩擦系数为1.0,那么推动重100公斤的滑块需要施加100公斤的力,推动重400公斤的滑块需要施加400公斤的力。如果摩擦系数为0.1,那么10公斤的力就可以推动重100公斤的滑块,而推动重400公斤的滑块也只需施加40公斤的力。
所以推动滑块所需的作用力与其重量成正比。滑块越重,推动它所需的作用力就越大。这一原理适用于制动器与离合器这样的装置,在这种装置上,制动片紧压着旋转盘。制动片受到的压力越大,汽车的制动力就越大。
| 摩擦系数 关于摩擦力的一个有趣现象是,推动物体所需的力通常比使其持续运动所需的力要大。两个接触面在没有发生相对位移的情况下存在一个静摩擦系数。如果两个接触面发生了相对位移,那么克服摩擦力所需的力就取决于动摩擦系数,动摩擦系数通常小于静摩擦系数。 就汽车轮胎而言,其动摩擦系数远小于静摩擦系数。所以,当轮胎接触面与路面没有发生相对位移时,汽车轮胎提供的牵引力最大。当轮胎打滑(如刹车或熄火)时,牵引力会大大降低。 |
在了解实际的汽车制动系统的各个部件之前,我们先来看看一个简单的系统:
可以看到,踏板到制动轴的距离是制动缸到制动轴距离的四倍,所以在踏板上施加的力在传递到制动缸之前就会被放大四倍。
还可以看到,制动缸的直径是连接踏板的液压缸直径的三倍,这又把制动力放大了九倍。综上所述,此系统把您脚部发出的力放大了36倍。如果您对踏板施加了10公斤的力,那么在车轮处挤压制动片的力将达到360公斤。
另一方面。这个简单的制动系统还存在几个问题有待解决。渗漏会导致什么结果?如果发生缓慢的渗漏,最终将导致制动缸内的制动液不足,制动系统也会随之失效。反之,如果发生急剧渗漏,您第一次刹车时所有的制动液就会喷射而出,制动系统就会完全失灵。
现代汽车中的主缸就是为了解决这一问题而设计的。请阅读主缸和组合阀工作原理一文。有关制动系统的其他文章,请参加下一页上的链接。
二 : 汽车制动系统讲解

汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解

汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解

汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解
汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解

汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解

汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解
汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解
汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解
汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解

汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解

汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解
汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解
汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解

汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解
汽车制动系统 汽车制动系统讲解

三 : GMS_通用汽车全球制造系统
INTRODUCTION TO
GMS
GMS
Global Operating System
GMS
GMS Executive Overview (4-5 Hours)
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 1
GMS
? Classroom Norms
1. Pagers, phones - Please turn off or put on vibrate 2. If urgent call, please talk outside 3. Relax, ask questions and have fun!!
?Standardized Introductions
1. Name 2. Role 3. Main hobby
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 2
What Do We Need To Do To Meet Our Vision?
Customer Satisfaction
GMS
Customer Enthusiasm
?
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
?
John S. Hamalian
Slide 3
Customer Satisfaction is not good enough!!!
Who is the Customer?
External Customer (Buys Product)
GMS
Customer Enthusiasm
Internal Customer (YOU!)
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 4
What Makes Customer Enthusiasm?
Good Buying Experience
GMS
+
Good Ownership Experience
=
Customer Enthusiasm
Sales Marketing
GMS Executive Overview
Design Engineering Manufacturing After Sales
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 5
What Does Everyone Need to Get Customer Enthusiasm?
GMS
Safe, Clean & Healthy Environment VW ? People-Oriented Organisation ? Attractive, High Quality Products Toyota ? Good Customer Response ? High Customer Value
?
Ford
GM
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 6
Needs Translate to Goals…
GMS
THE 5 MAIN GOALS
SAFETY (Safe Work) PEOPLE (Organizational Development) QUALITY (Attractive Product) RESPONSIVENESS (Quantity/ Volume/Speed) COST (Good Value)
$
Focus on employee Development, Involvement and Enthusiasm Each customer in each process expects a high quality product or service Eliminate waste and control costs to deliver our customers the right product at the right price!!
Safe, Clean & Healthy Working Environment for all employees and visitors
Customers want a quality product or service but they also want it FAST!
Provide every product or service (exactly what the customer wants) defect free, on demand, with no waste and in a work environment where everyone is happy and safe.
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 7
The Goal Sequence Has A Meaning!
GMS
Always Remember The Priorities…
C
TRADITIONAL
$
R
Q
P
S
Traditionally, the organisation was focused around financial controls with Quantity as a priority – People development and Safety were not particularly important
S
MODERN
P
Q
R
C
$
Modern philosophy is that Safety is always First with a priority on People and Quality. If we focus on these things, Cost through waste reduction - will eventually decrease
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
J Hamalian
John S. Hamalian
Slide 8
How Do We Reach Our Goals?…
GMS
GMS
Global Operating System
It is a critical p
hilosophy to achieve our Vision
“One System”
-One ‘Language’ - One Umbrella - One Company Culture - One Mindset
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 9
Creation of GMS
OPEL (Eisenach) QN
GMS
NUMMI (TOYOTA)
GMNA (Green Book)
CAMI (Suzuki) Saturn
GMS not a only a “GM” system but is mostly modeled on Toyota & some Suzuki philosophy
GMS
(1996)
GMS was born out of the strategic need to adopt modern, lean thinking for corporate survival
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 10
What is Lean Thinking?
Mass vs. Lean Processes
GMS
? Buffered processes are protected against everything: unexpected quality problems, stoppages, high absenteeism, etc. ? Lean processes assure continuous flow with minimal waste by empowered teams and the quality should be achieved within the process
1800 (Craft)
Production System
1900 (Mass) Buffered or Mass (“Fordism”)
2000 (Lean) Lean (Toyota)
Buffers & Waste
Standardization Leader Span of Control Planning & Problem Solving
High
High, by managers Narrow Low (reactive)
Low
High, by teams Moderate High (proactive)
Degree of Correction
Teamwork & Empowerment Risk
GMS Executive Overview
High (inspect-out quality)
Low Low
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
Low (built-in quality)
High High
John S. Hamalian
Slide 11
Toyota Philosophy
GMS
? Strong Corporate Culture
? Balance Between Process and Results ? Commitment to Learning not Knowing
? Entire Organisation Knows and Uses the System
? Minimum barriers between functions and levels ? Focus on Long Term Results Respect For Humanity and Continuous Improvement through the Elimination of Waste are Foundation of Toyota?s System
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 12
Use GMS Principles To Obtain Our Goals
GOOD PROCESSES
Vision/ Mission
GMS
GOOD RESULTS
? Safety Goals & Metrics ? People (Results) ? Quality ? Responsiveness ? Cost
Business Goals (Scorecard )
Lean Principles (Process)
Standardization
Built-In-Quality
Short Lead Time
Continuous Improvement Company People Involvement Company
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
Methods to Meet the Goals (GMS)
John S. Hamalian
Slide 13
THE 5 GMS PRINCIPLES
People Involvement
People are the most valuable resource in the company
GMS
Standardization
Set and follow standards to achieve a base from which to grow Customer’s Quality expectations are built in to each process to ensure defects are not passed Reduce the time to deliver any product or service
Built-In-Quality
Do not
Accept Build Ship
a Defect!
Short Lead Time Continuous Improvement
GMS Executive Overview
$
Foster a culture of change and constant improvement
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 14
A Company-Wide Operating System based on Lean Business Principles
GMS
Like An Atom We Need A
ll The Pieces Working Together!!
GMS
“One Company” – One System
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 15
The 33 Elements Work Together
GMS
Like A Jigsaw Puzzle You Need All The Pieces So It Can Work
GMS
Vision
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Simple Process Flow
Values
Health and Safety Priority Manufacturing Process Validation ???? ??
Team Concept Product Quality Standards
Fixed Period Ordering System/ Order Parts
Management by TAKT TimeTAKT ???? Workplace Organization
Quality Feedback/ FeedForward Level Vehicle Order Schedule
Controlled External Transportation ??? ?? ??
Andon Concept Total Productive Maintenance
Quality System Management
Scheduled Shipping / Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Internal Pull / Delivery
Supply Chain Management
Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Tooling and Layout
Continuous Improvement Process
Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 16
4
GMS CASE STUDY
General Motors North America:
GMS
Before GMS: 1996
SPQRC
GMS
After GMS:
2003
SPQRC
BUT!!!…Toyota still enjoys 8% net profit while GM is at 1.5%
GM needs to outperform Toyota by US$1,500 – $2,000 / unit…
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 17
4
GMS as an Enterprise-Wide System
GMS is a common operating methodology that can be used anywhere in the organisation
Engineering
GMS
Manufacturing
Purchasing & Suppliers
SPO
Powertrain
Avoid the ‘Silo Syndrome’
Take an Integrated Approach Link the Functional Groups Together Used in Manufacturing but Principles are Generic
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
J Hamalian
John S. Hamalian
Slide 18
A Common ?Language? and Company Culture throughout the entire Customer Chain
GMS
Lean Business Principles
Designers & Product Engineering After-Sales & Dealers
Production
Sales & Marketing
Purchasing & Suppliers
Buyers
“One Company” with Customer First
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 19
What is a ?Factory??
A place where a repeatable process is conducted in which there are inputs, internal activity and outputs
GMS
New Vehicle Factory
New Advertisement Factory
Expense Report Processing Factory
Purchasing Order Process Factory
Service Center Factory
Who are ?Operators??
Anyone who works in a highly repeatable job and requires support to be effective
Paradigm Shift: We have to think of the work we all do in terms of a common process methodology 5 Everyone Can Use Lean Business Principles
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 20
People Involvement
GMS
? People Involvement Elements
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Vision Values Health
& Safety Qualified People Teamwork People Involvement Open Communication Leadership Behavior (Shop Floor Management)
GMS
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 21
GMS
Fish Philosophy Video
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 22
GMS
Fish Philosophy Video Discussion
?
What GMS concepts did we see in the video? Discuss as an open forum
?
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 23
Fish Philosophy Video Discussion
Environment At The Fish Company Enables:
?People Involvement/Employee Enthusiasm
?Teamwork ?Low Absenteeism ?Job Rotation/Flexibility….
GMS
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 24
People Involvement Company
GMS
PEOPLE are our most important resource!!!
Fruit = Quality Product Branches = Processes & Tools (GMS Elements)
Trunk = People & Mindset
Roots = Culture, Values & Philosophy (GMS Principles)
Soil = Environment
Like a Tree, People Need Nurturing for Growth
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 25
Change In Thinking
TRADITIONAL
VIP #1
GMS
MODERN
TEAM MEMBER #1
Team Member
Directors
Team Leader Group Leader Mgr
Managers
Supervisors
Operators
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 26
Leadership Mind Change
TOP-DOWN LEADERSHIP STYLE
Direction Support
GMS
MODERN LEADERSHIP MINDSET
TWOWAY STREET
Direction Support
80%
20%
20%
80%
J Hamalian
Give Orders
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
Teach & Coach!!!
John S. Hamalian
Slide 27
Employee Mind Change
TRADITIONAL EXPECTATION ? Just Do What You Are Told To Do MODERN EXPECTATION ? Participate in Making Standardized Work
GMS
? Employee Enthusiasm Not Important
? Continuously Improve Job
? Involved in Problem Solving ? Involvement Brings Enthusiasm!
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 28
GMS
People Involvement Company
Effective Communication ? Empowerment
? Trust
? Teamwork/ Cooperation
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
? Mutual Respect
John S. Hamalian
Slide 29
People Involvement
Health and Safety Priority
GMS
Vision/ Mission Values
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Simple Process Flow Andon Concept
Health and Safety Priority
Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time Workplace Organization
Product Quality Standards
Team Concept Period Fixed Ordering System/ Order Parts Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Controlled External Transportation
Total Productive Maintenance
Quality Scheduled System Shipping / Management Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Internal Pull / Delivery
Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Continuous Improve
ment Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Process Supply Tooling and Layout Chain Management Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 30
Health and Safety
“We are committed to protecting the health and safety of each employee as the overriding priority of the Corporation”.
> Our goal is:
GMS
ZERO Incidents!!
Group Discussion:
What is an ?Incident? vs. an ?Accident??
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 31
Building a “Safety Culture”
The Stages of Safety Awareness
No Problem – He Can Still Work!
GMS
Stage 1: Unawareness of Hazards
Stage 2: Awareness But No Action to Prevent Injury
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
Stage 3: Injury But Still No Concern
GMS Executive Overview
John S. Hamalian
Slide 32
Building a “Safety Culture”
The Stages of Safety Awareness
SPQRC
GMS
Stage 4: Injury and Realisation of Impact to Person and Company
GMS Executive Overview
Stage 5: Awareness of Hazards & Proactive Countermeasures to Prevent Incidents
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 33
Heinrich Hazard Pyramid
Most Reactive
GMS
Employee Hits Head on Edge of Desk While Falling. Breaks Neck. Dies. Employee Fractures Arm While Hitting the Floor. Two Weeks Out of Work. While Falling, employee?s Body Grazes Edge of Metal Drawer and Lacerates Arm. Requires Four Stitches Employee Slips on Coffee Employee Spills Coffee on Floor and Walks Away
1
Fatality
Lost Workday Injury
300
Reactive
Recordable or First Aid Injury
3,000
Proactive
Near Miss
30,000
Most Proactive
Potential Hazard / Unsafe Situation
Herbert Heinrich Travelers Insurance Co.
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 34
Health and Safety
? How
GMS
Can We Achieve Our Goal of zero First Aid Injuries, Recordables or Lost Work Days?
- Incident Prevention (Building a Safety “Culture”)
- Incident Reporting, Tracking and Resolution (encourage honest, open reporting to enable Problem Solving & avoid repeat incident)
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 35
GMS
Health and Safety
Incidents can be Prevented through these five activities and more:
?
?
? ?
?
Behavior Workplace Organization/5S Personal Protective Equipment Safe Use of Hazardous Materials Ergonomics
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 36
People Involvement
Team Concept
GMS
Vision/ Mission Values
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Simple Process Flow Andon Concept
Health and Safety Priority
Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time Workplace Organization
Product Quality Standards
Team Concept Period Fixed Ordering System/ Order Parts Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Controlled External Transportation
Total Pro
ductive Maintenance
Quality Scheduled System Shipping / Management Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Internal Pull / Delivery
Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Continuous Supply Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Improvement Chain Tooling and Layout Process Management Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 37
Teamwork
GMS
What is a Team?
Group Discussion:
HOW DO YOU ACHIEVE REAL TEAMWORK?
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 38
Team Concept
GMS
Small groups of empowered people who share common goals and support each other through common tasks
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 39
Team Concept
GMS
Team Member
The Organization Structure Is Designed To Support Small, Empowered Teams
Team Leader Group Leader & Support Areas
Leadership
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 40
Team Concept
?
GMS
Common SPQRC goals and regular team meetings. Empowerment to make decisions within spans of control Responsibility for: – Making Standardized Work – Problem Solving – Continuous Improvement
?
?
?
Job Rotation is generally performed
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 41
A Single Team Can Only Be Successful If The Big Team Wins!!…
Individual Family
GMS
Quality Purchasing Design
Human Resources Engineering Unions PC&L Finance Suppliers
Company
Manufacturing Information Systems
Sales & Marketing
Nation & World
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 42
People Involvement
GMS
Vision/ Mission Values
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Simple Process Flow
Health and Safety Priority Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time
Team Concept Product Quality Standards
Fixed Period Ordering System/ Order Parts
Controlled External Transportation
Andon Concept Total Productive Maintenance
Quality Feedback/ Feedforward Level Vehicle Order Schedule s
Quality System Management
Scheduled Shipping / Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Workplace Organization
Internal Pull / Delivery
Supply Chain Management
Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Tooling and Layout
Continuous Improvement Process
Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 43
Qualified People
Our People Will Be. . .
? ? ? ? ?
GMS
Empowered/Engaged/Energetic Knowledgeable Flexible/Open-Minded Customer Oriented Skilled in the Continuous Improvement Process and Problem Solving Able to Work in Teams
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
?
GMS Executive Overview
John S. Hamalian
Slide 44
GMS
Qualified People
Job Improvement & Growth
People Development
Job Performance Fee
dback
Training
Hiring/ Assessment
Time
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 45
GMS
WE LEARN
10% of what we read 20% of what we hear 30% of what we see 50% of what we see and hear 70% of what we discuss with others 80% of what we experience personally 95% of what we teach to someone else
William Glasser
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 46
Training Methodology
JOB INSTRUCTION TRAINING (JIT)
GMS
The Four Steps of JIT
Confirmation Awareness
Step 4: FOLLOW UP
(Trainee Confirm Skill)
A
P
Step 1: PREPARE TRAINEE
(Study Standardized Work)
HEAR SEE DO
Step 3: TRY OUT PERFORMANCE
(Trainee Do, Trainer Watch) Skill
Why – What – How!!!
C
D
Step 2: PRESENT OPERATION
(Trainer Do, Trainee Watch) Knowledge
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 47
People Involvement
People Involvement
GMS
Vision/ Mission Values
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Simple Process Flow
Andon Concept
Health and Safety Priority
Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time Workplace Organization
Product Quality Standards
Team Concept Period Fixed Ordering System/ Order Parts Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Controlled External Transportation
Total Productive Maintenance
Quality Scheduled System Shipping / Management Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Internal Pull / Delivery
Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Continuous Supply Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Improvement Chain Tooling and Layout Process Management Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 48
People Involvement Element (Involvement & Recognition)
Create and maintain an environment which fosters a “spirit of pride”
GMS
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 49
Involvement & Recognition
There are three aspects of Involvement & Recognition:
GMS
1. Individual & Team Ideas 2. Small Group Programs 3. Rewards and Recognition
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 50
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
GMS
Vision/ Mission Values
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Simple Process Flow
Andon Concept
Health and Safety Priority
Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time Workplace Organization
Product Quality Standards
Team Concept Period Fixed Ordering System/ Order Parts Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Controlled External Transportation
Total Productive Maintenance
Quality Scheduled System Shipping / Management Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Internal Pull / Delivery
Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Continuous Supply Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Improvement Chain Tooling and Layout Process Management Probl
em Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 51
GMS
Open Communication Process
? Leaders must drive communications ? Actively engage employees in the business openly & frequently ? Open-Door Policy ? Listen Often ? Have a Physical Presence (MBWA – Management By Walking Around)
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 52
Guiding Principles
WHAT - HOW - WHY? Traditionally, communication only focuses on the “WHAT” and maybe the “HOW”, but people deserve to know the “WHY”!!!
GMS
EVEN IF THEY DON’T AGREE AT LEAST THEY WILL UNDERSTAND!!!
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 53
Key Enablers
Effective Use Of Media
BEST!!
Core Level Face-to-face Communication
Communication Boards Satellite Broadcasts State of the Business Mtg. Team Mtg. Internet / Intranet Job Postings
GMS
BETTER
Level One Face-to-many faces Communication
Group Training
Teaching Coaching Training Feedback
Business Update Mtg.
Team Boards
Dept. Head?s. Mtg. Diagonal Slice Mtg. E-mail
GOOD
Newsletters
Make a Communication Plan!
GMS Executive Overview
Voice Mail
Level Two Informational Communication
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 54
People Involvement
Shop Floor Management
GMS
Vision/ Mission Values
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Simple Process Flow
Health and Safety Priority
Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time Workplace Organization
Product Quality Standards
Team Concept Period Fixed Ordering System/ Order Parts Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Controlled External Transportation
Andon Concept
Total Productive Maintenance
Quality Scheduled System Shipping / Management Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Internal Pull / Delivery
Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Continuous Supply Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Improvement Chain Tooling and Layout Process Management Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 55
Leadership Behavior
(Shop Floor Management)
GMS
Go and See Leadership Style Lead By Example SPQRC-based Meeting Structure Proactive Communication Process Regular Checks of Processes
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 56
Go and See Leadership Style
GMS
The focus of leadership is on the places where work is performed. This is accomplished through the “Go and See” philosophy:
Go and See the work areas where concerns exist and to check progress
“Don?t just sit at your desk, go and see what is happening!!!”
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 57
Lead By Example
For Example – If You Want People to Keep Their Area Clean, You Had Better Also Keep YOUR Area Clean!!!
GMS
Leader
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 58
GMS
I Love Lucy Video Part I
(Stop video before Chocolate Assembly Line)
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 59
GMS
I Love Lucy Video Discussion
?
What GMS concepts did we (not) see in the video? (at home and at the job!) Discuss as an open forum – not by teams
?
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 60
I Love Lucy Video Discussion
What did we see in the video:
?Lack of Teamwork: ? At home, spouses did not understand each other?s jobs ? No teamwork at factory
GMS
? Boss was traditional top-down style, not a leader
?Lack Of Qualified People: ? Job qualifications not clear, poor screening process ? Lucy & Ethel not qualified for job ? Lucy & Ethel received poor training by boss
?Lack of Open Communication:
? Spouses did not communicate enough (example – at breakfast) ? No talking at factory results in no support & no teamwork
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
J Hamalian
John S. Hamalian
Slide 61
GMS
Vision
Shop Floor Management
Values
Health and Safety Priority Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time
WASTE
Team Concept Product Quality Standards Fixed Period Ordering System/ Order Parts Quality Feedback/ Feedforward Level Vehicle Order Schedul es Quality System Management Scheduled Shipping / Receiving Internal Pull / Delivery Supply Chain Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Simple Process Flow Andon Concept Total Productive Maintenance
Controlled External Transportation
Business Plan Deployment
Workplace Organization
Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Tooling and Layout
Continuous Improvement Process
Problem Solving
Vision
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Simple Process Flow
Values Health and Safety Priority Manufacturing Process Validation Product Quality Standards Team Concept
Fixed Period Ordering System/ Order Parts
Controlled External Transportation
Andon Concept
Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Quality System Management
Management by TAKT Time Internal Pull / Delivery Level Vehicl e Order Sche dules
Scheduled Shipping / Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Total Productive Maintenance
Workplace Organization
Supply Chain Management
Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Tooling and Layout
Continuous Improvement Process
Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 62
GMS
How Often Do We See These Scenarios in Our Work Area?
Stocking Up Inventory
Excess Walking
Equipment Breakdown
Excessive Transporting, Storage & Handling
Decision Communication and Reporting Maze
Meetings, Meetings, Meetings!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version D
ate 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 63
GMS
Enemies of Any Process
Three Enemies:
7 Wastes
(Muda), Unevenness (Mura), and Overburden (Muri)
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 64
7 TYPES OF WASTE
Sending back forms for incomplete or inaccurate data CURRENT Processing excessive written THINKING communication to determine Shift issues requiring attention (mental processing)
Mindset
Producing reports that are not GMS used, performing more analysis than required, producing reports before they REQUIRED needed are THINKING
Correction
Processing
P
C
WASTE
Keeping multiple copies of reports
Inventory
Over Production
I
W
Waiting
TYPES OF WASTE
O M
Motion
M
Material Movement
Delays in getting needed information, approvals, or decisions
Searching for misplaced items
WASTE NOT DEFINED WASTE IS "TANGIBLE" Filing documents that will REACT TO LARGE EXAMPLES IDENTIFY never be used again MANY SMALL OPPORTUNITIES REACTIVE IMPROVEMENT LEADS TO LARGE OVERALL CHANGE CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 65
GMS
Waste is EVERYWHERE!!!
Waste Elimination through People Involvement is the Foundation of the entire Operating System
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 66
Make Waste Visible & Conquer It!
GMS
There are two major categories of waste: 1. Obvious waste 2. Hidden waste.
Most Waste is Hidden
Waste is easy to identify in a well organised organisation
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 67
Why Eliminate Waste?
Poor companies let waste slowly build up then realize they are in trouble and make huge cuts that affect value-added activities and people?s livelihood. Successful companies continuously eliminate waste From all processes and actually GROW the company!!
GMS
Example: Toyota
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 68
GMS
Eliminating Waste Is Job Security
WASTE
$
MORE MONEY FOR VALUEADDED THINGS BETTER PRODUCTS, BETTER FEATURES, MORE ADVERTISING
INCREASED SALES, INCREASED DEMAND, MORE PRODUCTION, MORE JOBS
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 69
Standardization
GMS
?
Standardization Elements
Standardized Work Workplace Organization Management By Takt Time Visual Management
? ? ? ?
GMS
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 70
Standardization
The purpose of standardization is to reduce variation and stabilize, so as to achieve a base from which to grow and improve.
World Class
GMS
Change
“THE WEDGE” TO STABILIZE BEST PRACTICE
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 71
Standardization
A Standard Is The Best Current Practic
e Based On Many People?s Experience & Lessons Learned, so…
GMS
DON’T SHORTCUT THE STANDARD!!!
BAD THINGS COULD HAPPEN, ESPECIALLY SAFETY & QUALITY PROBLEMS
Standard
IF YOU DON’T LIKE THE STANDARD, TRY TO CHANGE IT, BUT NEVER SHORTCUT IT….
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 72
GMS
What Happens When We Do Not Follow Standards???
EVERY YEAR PEOPLE DIE FROM NOT FOLLOWING LOCK-OUT PROCEDURE
U.S SUBMARINE HITS JAPANESE FISHING BOAT SURFACING PROCEDURE NOT FOLLOWED
GERMAN PLANE CRASHES IN SWITZERLAND – AIR TRAFFIC CONTROL PROCEDURES IGNORED
EXXON VALDEZ OIL SPILL – CAPTAIN DID NOT FOLLOW STANDARDS
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 73
GMS
MAKE RULE
TEACH RULE KEEP RULE
It is easy to make standards, but we do not always do a good job communicating them and are even worse at sustaining them (including ourselves)
If you do not have a process to sustain a standard – why even introduce it in the first place?
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 74
People Involvement Link to Standardization
■ Results achieved only when people all do the right thing
GMS
Lack of Discipline results in Chaos
GMS Executive Overview
Discipline and Orderly Environment
I.S. Han - RBPS
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 75
Standardization
Workplace Organization
Shop Floor Vision/ Management Mission Health and Safety Priority
GMS
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Values
Simple Process Flow Andon Concept
Team Concept Period Fixed Ordering Controlled System/ External Order Parts Transportation Scheduled Quality Shipping / System Receiving Management
Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time
Product Quality Standards
Total Productive Maintenance
Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Business Plan Deployment
Workplace Organization
Internal Pull / Level Vehicle Delivery Order Schedules
Lean Design of Facilities, Supply Equipment, Chain Tooling and Layout Management
Continuous Improvement Process
Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 76
GMS
WPO Motto: “A place for everything and everything in its place”
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 77
Workplace Organization
Put order to the workplace by making Standards that allow “out-of-standard” conditions to be visible!!
GMS
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 78
GMS
How is workplace organization done?
Workplace Organization
5S
1 Sift/Clear
GMS Executive Overview
5 Self Discipline/ Cont. Improvement
4 Sustain/Maintain 3 Sweep/Clean 2 Sort/Standardize
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 79
GMS
Why workplace organiz
ation?
WPO is a key means of visualizing and eliminating waste
Anything outside the standard is WASTE!!!
Make Waste Visible!!!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
J Hamalian
John S. Hamalian
Slide 80
GMS
Why workplace organization?
SAFETY
Good 5S Leads to Good Safety! trip, slip hazards, etc.
No
QUALITY
Items always in same place means less likely to make mistakes
COST
Items always in same place means less wasteful and more repeatable motions
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 81
Example of 5S
Which Cabinet Do You Want?
GMS
(Which one is Safer, makes Waste visible, leads to less Mistakes and lets you get parts Quicker?)
Cabinet “Before 5S”
Cabinet “After 5S”
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 82
Standardization
Management by TAKT Time
GMS
Vision/ Mission
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Values
Health and Safety Priority
Open Communication Process Team Concept
Small Lot Packaging
Simple Process Flow
Fixed Period Controlled Ordering External System/ Transportation Order Parts
Andon Concept
Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT WorkTime place Organization
Product Quality Standards
Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Quality Scheduled System Shipping / Management Receiving Lean Design of Facilities, Supply Equipment, Chain Tooling and Layout Management
Total Productive Maintenance
Business Plan Deployment Continuous Improvement Process
Internal Pull / Delivery
Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 83
Time Management Philosophy
GMS
Instilling A Sense Of Time & Discipline to Keep It
No Time Management: No Agenda 1) Meeting Time 2) Meeting Place 3) Participants (Leader has no regard for time)
? No Sense of Time Built in Process ? Some arrive late, others have to wait ?No ?timekeeper? to keep discipline ? Meeting can easily go over time thus producing waste
GMS Executive Overview
Management By Takt: Agenda with Time 8:00 Introductions 8:10 Kick-off 8:30 Team Activity 11:00 Report-Outs
(Leader Keeps Time)
? Sense of Time Built In to the process ? All members have a Respect for time ? Leaders ensure Discipline ? Keeping time minimizes Waste
J Hamalian
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 84
Management By Takt Time (Time Management)
Takt Time: – The Required Amount Of Time To Produce a Product Or Service Based On Customer Demand
Takt Time =
Operational Time Per Period Number of goods or services required per time period
GMS
Relate all Work to Time and Make it Visual and Manageable!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 85
Management By Takt Time (Time Management)
Operation
Take-Off
GMS
Example: Airliner
60’
Flight Attendant has 60’ to s
erve drinks – if there are 60 passengers, Takt Time = 1’)
30’
Serve Drinks
90’
Landing
Meeting
Kick-Off
Example: Board Meeting
8 Hours
Quarter Review
Lunch
Next Steps
Wrap-Up
Project
Concept
Example: Marketing
3 months
Approval
Production Ready
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
Advertisement shown on T.V.
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
John S. Hamalian
Slide 86
Standardization
GMS
Vision/ Mission
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Values
Health and Safety Priority
Fixed Period Team Concept Ordering System/ Order Parts
Simple Process Flow Controlled External Transportation
Andon Concept
Manufacturing Process Validation
Product Quality Standards
Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Quality System Management
Total Productive Maintenance
Management by TAKT Time Workplace Organization
Scheduled Shipping / Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Internal Pull / Delivery
Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Supply Chain Management
Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Tooling and Layout
Continuous Improvement Process
Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 87
GMS
Visual Management Key Concepts
MAKE STANDARD & OUT OF STANDARD CONDITIONS CLEAR & VISIBLE!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
x
x
J Hamalian
John S. Hamalian
Slide 88
GMS
Visual Management Key Concepts
STATUS AT A GLANCE
GUIDELINE – SHOULD NOT TAKE MORE THAN ONE SECOND TO GRASP ANY SITUATION!
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 89
GMS
“A Picture Is Worth A Thousand Words.”
Get Standards Out From the Desk and Into the Open!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 90
Example
GMS
Which visual method communicates information (how much time is left for walking) better?
Stack Light
WALK DON?T WALK
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 91
GMS
Standardization
Vision/ Mission
Shop Floor Management Health and Safety Priority
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Values
Simple Process Flow Controlled External Transportation Andon Concept
Team Concept Period Fixed Ordering System/ Order Parts Quality Quality System Feedback/ Management Feedforward Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time Workplace Organization
Product Quality Standards
Total Productive Maintenance
Scheduled Shipping / Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Internal Pull / Delivery
Supply Lean Design of Facilities, Chain Equipment, Management Tooling and Layout
Continuous Improvement Process
Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 92
Standardized Work
The documented, current best method to Safely and
Efficiently perform any repeatable process that meets the necessary level of Quality
GMS
Production
Office
Standardized Work Can Be Performed Everywhere!!!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 93
GMS
Standardized Work
Without Standardization
With Standardization
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 94
GMS
Each Individual Has Good Ideas – If We Do Not Document The Best Methods Then We Are Not Fully Utilizing The Team?s Brainpower and We Will Never Improve Or We May Actually Get Worse!!!
Without Standardized Work We Are Destined To Repeat The Same Mistakes Over and Over Again!
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 95
GMS
Would You Want To Get Into A Plane Where The Crew Did Not Exactly Follow A Standardized Check Process??? – Even Though They Have Performed It Hundreds Of Times!!! 1. Check Fuel 2. Check Tires 3. Check Instruments
Nobody’s Memory is Perfect - Have the Discipline to follow Standardized Work. Don’t Get Complacent!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
J Hamalian
John S. Hamalian
Slide 96
GMS
Lego Exercise
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 97
Built-In-Quality
GMS
?
Built-In Quality Key Elements
Customer Quality Standards Process Validation/Change Control In-Process Control Feedback/Feedforward Communication
? ? ? ?
GMS
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 98
Built-In-Quality
GMS
?
What Is Quality? Group Discussion
?
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 99
Definitions
GMS
?
Quality is what the customer perceives to be acceptable to achieve his/her enthusiasm
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 100
Poor Quality Means Lost Sales
GMS
Mad Cow
Firestone
uninstalled shift lock (Sudden Acceleration)
(Unintended Accidents)
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 101
Built-In-Quality
? What is Built-In-Quality?
? Group Discussion
GMS
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 102
What is Built-In Quality?
Understand Your Supplier and Customer and build quality INTO the process through Prevention, Detection and Containment so defects are not passed to the customer!
GMS
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 103
The Customer Chain Satisfy Your Customer…
Design & Engineering Production Sales & Marketing
GMS
Dealers
Suppliers Buyers
Every Process Has at Least One “Customer” and One “Supplier”
Who is Your Customer?
Who is Your Supplier?
- Group Discussion
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
GMS Executive Overview
John S. Hamalian
Slide 104
Built-In-Quality Motto
Satisfy Your Customer…
GMS
Do not
Accept Build Ship
a Defect!
Solve Problems Through Teamwork!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 105
Don’t run away from the problem!
What water leaks? I don?t see any water leaks
This car wasn?t made on my shift
I won?t run any trial until I have an assembly method from Engineering and the manpower. The problem is Press Shop. The flange is too long.
GMS
It is not from my area, maybe it?s the sealer
The problem is that the pieces are bad from the supplier.
Quality Through Teamwork – Know Your Customer!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 106
Always Remember The Priorities…
GMS
Customer Enthusiasm! Safety People Quality Responsiveness Cost Quality is the Key to Our Survival – We Will Not Maintain Global Auto Leadership without it and it Involves Each and Every One of Us, Day in and Day Out
J Hamalian
Importance
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 107
GMS
Feedback/Feedforward
Process A
Process B
Process C
“Suppliers”
You
“Customer”
Reactive
Proactive
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 108
GMS
I Love Lucy Video Part II
(Start video at Chocolate Assembly Line)
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 109
I Love Lucy Video Discussion
What did we see in the video:
? Lack of Standardized Work: ? No documented standardized work on job ? No standardized work to use as basis for training
GMS
? No quality standard for completed chocolate
? Lack Of Management By Takt Time: ? Takt Time arbitrarily changed ? No communication or planning of Takt Time change ? No visual indication of workstation beginning and end
? Lack of Built-In Quality:
? No way to call for help ? No way to stop line or prevent defects from leaving station
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
J Hamalian
John S. Hamalian
Slide 110
Short Lead Time
GMS
? Short Lead Time Key Elements ? Simple Process Flow ? Pull System Concept ? Level Scheduling
GMS
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 111
Short Lead Time
GMS
The Relentless Pursuit to Reduce the Amount Of Time To Produce a Product Or Service
Achieve Customer Enthusiasm by delivering more quickly and reducing costs, while maintaining quality
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 112
GMS
Philosophy
Process Thinking at Toyota
“Brilliant process management is our strategy” “We get brilliant results from average people managing brilliant processes”
Toyota Observes that…
“… our competitors often get average (or worse) results from brilliant people managing b
roken processes.”
James Womack
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 113
Short Lead Time
Guiding Principles Simple Process Flow “The Perfect Process”
GMS
“Simple Sequential Process Flow of Material and Information”
? Identify Customer Requirements ? Relate Work to Time ? Make Process Flow & Waste Visual ? Use First In First Out (FIFO) ? Pull from Customer, not Push from Supplier ? Establish Rhythm (level scheduling) in Small Lots ? Make Progress/Delays Visual
One Key Tool is “Value Stream Mapping”
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 114
Understanding the flow determines where to apply Process Improvements
GMS
Flow
Flow Restrictors
Theory of Constraints
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 115
Value Stream Mapping
What is a Value Stream?
A value stream involves all the steps, both value added and non value added, required to complete a product or service from beginning to end
GMS
What is a Value Stream Map?
A value stream map follows a product?s production path from beginning to end, and provides a visual representation of every process in both the material and information flows.
Make The Process Visual!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 116
Value Stream Maps Enable a System View
Scoping the Value Stream
GMS
Determine the Value Stream to be improved Understanding how things currently operate. This is the foundation for the future state.
Current state drawing
Future state drawing
Designing a lean flow through the application of GMS principles
The goal of mapping!
Planning and Implementation
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 117
Jack?s Taxes - Current State
Client
40 clients
GMS
Send reminder
IN
Sort receipts & documents
Prepare worksheet
Confirm deductions
IN Jack P/T 30 min W/T --FTQ 10%
3 weeks
TS
IN
3 days
Print & Collate TS forms
Review & sign forms
Mail forms
IN
3 days
IN
1 day
1 week
John P/T 10 min W/T --FTQ 100%
Jack P/T 60 min W/T 1 week FTQ 95%
Jack P/T 10 min W/T 1 week FTQ 50%
John P/T 15 min W/T --FTQ 98%
Jack P/T 15 min W/T --FTQ 100%
John P/T 10 min W/T --FTQ 100%
P/T W/T FTQ
10 min 100 %
30 1 week min 10 %
3 weeks
60 min 1 week 95 %
10 min 1 week 50 %
3 days
15 min 98 %
3 days
15 min 100 %
1 day
10 min 100 %
140 min 7 wks, 2 days 4.7 %
Total Lead Time:
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
7 wks, 2 days, 140 min
Slide 118
John S. Hamalian
Jack?s Taxes – Process Improvement
Client
40 clients
? Customer ? Work
requirements? flow smoothly? GMS ? Trigger & sequence work? ? Rhythm (leveling)? ? Progress & delays visible? ? Process improvements?
Takt Time = Available time / Customer Requirements
= 40 days / 40 Clients = 1 per day
Stand. Work
S
end reminder Sort XOXO receipts & documents Prepare worksheet TS Confirm deductions Print & Collate TS forms
FIFO
Review & sign forms
Mail forms
IN
IN Jack P/T 30 min Data entry W/T --Worksheet FTQ 10% training
3 weeks
IN
IN
3 days
IN
1 day
1 week
COMBINE PROCESSES 3 days
John P/T 10 min W/T --FTQ 100%
P/T W/T FTQ
10 min 100 %
30 1 week min 10 %
min 3 Individual weeks 1 week
Jack John Jack John P/T 60 min P/T 10 min P/T 15 min W/T 1 week W/T 1 week W/T --FTQ 95% FTQ 50% FTQ 98% Reduce process time to 75 min Standardize Work 15 60 10
min 1 week 50 % 3 days min 98 %
Jack P/T 15 min W/T --FTQ 100%
John P/T 10 min W/T --FTQ 100%
3 days
15 min 100 %
1 day
10 min 100 %
140 min 7 wks, 2 days 4.7 %
1040, 1040EZ 95 % training
Total Lead Time: 7 wks, 2 days, 140 min
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
GMS Executive Overview
John S. Hamalian
Slide 119
Customer Requirements:
?Tax Forms completed accurately ?Finished before filling time ?Lowest possible cost
Jack?s Taxes Future State
Client
40 clients 1 per day Over 8 weeks
GMS
Takt Time = Available time / Customer Requirements = 40 days / 40 Clients = 1 per day
max 1 day Send Reminder IN John P/T 10 min
W/T FTQ 100%
P/T W/T FTQ 10 min
max 1 day Check & sign forms IN Jack P/T 15 min W/T 1 day FTQ 100%
15 min
XOXO
Data entry + print FS forms John P/T 75 min
W/T FTQ 98%
75 min
FIFO
Mail forms
John P/T 10 min W/T 1 day FTQ 100%
10 min 1 day 100 min 2 days
1 day
100 %
98 %
100 %
100 %
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
98 % 2 days, 100 min
Slide 120
3 Areas of Short Lead Time
Total Lead Time (Order To Delivery)
Receive Order To Delivery of Product and Receive Payment (O.T.D.)
GMS
Process Lead Time (Lean Materials) Product Lead Time
From Raw Material to Final Assembly
Reduce Lead Time to Produce Any Good Or Service
Examples: ? Product Development (Concept to SOP) ? Budget Development ? Marketing Clinic Feedback
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 121
Continuous Improvement
GMS
? Continuous Improvement Key Elements
? ? ? ? Business Plan Deployment Problem Solving Andon Concept Continuous Improvement Process
GMS
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 122
Continuous Improvement Company
No Company Today Can Survive Without Having All Employees Focused on Continuous Improvement
GMS
Small, steady improvements to constantly improve The Standard!!
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 123
Build a Continuous Improvement Culture
Poor Organisations Resist Change and Become Stifled and Stale – Great Organisations Embrace Change and Constantly Look for Ways to Improve
GMS
”The Only Constant is Change”
Never Be Satisfied With The ?Status Quo?!
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date
2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 124
Continuous Improvement
GMS
Standardized Work Is A Baseline for Many, Small Continuous Improvements!!!
Improvement Improvement
Improvement
Standardization Standardization
Standardization
Standardization
Once the Improvement is Validated, Update the Standard!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 125
The PDCA Cycle
PDCA is a Fundamental Concept Throughout GMS
GMS
Grasp the Situation
Plan
Action
Do
Check
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 126
The PDCA Cycle is One Of The Most Important Concepts In A Company
Poor companies do little planning, mostly doing, do not check their status and then react to everything…
GMS
P
D
REACT
Or, they do a lot of Planning and no Execution or check system which again leads to Reaction or lack of Improvement…
? ?
J Hamalian
P
D
REACT
World-Class companies do excellent planning, always perform checks that enable taking corrective action and stay on schedule…
P
D
C
A
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 127
PDCA Can Be Used For Anything
Our Family Has Not Had A Vacation In A Long Time!
GMS
Grasp the Situation
Let?s go to the Beach!!!
Plan
Fix oil leak & leave on time Prepare for the trip
Action
Two days before leaving, check engine – OIL LEAK!
Do
Check
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 128
GMS
Continuous Improvement
Business Plan Deployment
Vision
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process Team Concept
Small Lot Packaging
Values
Health and Safety Priority Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time Workplace Organization Internal Pull / Delivery In-Process Control and Verification
Simple Process Flow Andon Concept
Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Fixed Period Ordering System/ Order Parts Quality System Management
Controlled External Transportation
Scheduled Shipping / Receiving
Total Productive Maintenance
Business Plan Deployment
Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Supply Chain Management
Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Tooling and Layout
Continuous Improvement Process
Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 129
Before BPD…
? ? ?
Leader
GMS
?
no ownership
ONLY (S)HE KNOWS THE GOALS…
?
?
no regular reviews
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
GMS Executive Overview
John S. Hamalian
Slide 130
After BPD…
GMS
REGULAR COMMUNICATION
CLEAR TARGETS
VISION
TRACK PERFORMANCE
Leader
DEPLOY RESOURCES
EVERYONE KNOWS THE GOALS…
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
COMMON GOALS
CLEAR DIRECTION
GMS Executive Overview John S. Hamalian
GME-BPD Guide
Slide 131
Achieving Our Vision
In order for GM to achieve Its VISION, we have to achieve our Goals…
GMS
Vision/ Mission
Concr
ete GOALS (SPQRC)
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
CLEAR & MEASURABLE TARGETS A METHOD TO RESEARCH THE TARGETS
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 132
Who is involved in BPD? – Everyone!!!
Why Engage the Workforce?
Why? Why?
% of People Involvement
GMS
Why? Why?
Why?
50% 40% 30% 20% 10%
1-6 6-10 10-20 20-40 40-100
% of Possible Improvement
No ?One Person? Has All the Best Ideas!!!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 133
The Cascading Process
Level 4 Team ? Clear Targets ? Review Process
GMS
Level 3 Group Leader ? Action Plans ? Clear Targets ? Review Process
Level 2
Department Manager
Level 1 Top Leadership ? Mission/Strategy ? Goals & Objectives ? Clear Targets ? Action Plans ? Review Process
? Goals & Objectives ? Clear Targets ? Action Plans ? Review Process
Each Level of Leadership Must Hand Down Simple & Clear Targets to Their Team…
Go Down To The Lowest Level!!!
S.M.A.R.T. Targets: Specific, Measurable, Aligned, Realistic & Timed
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 134
GMS
If You Can?t Measure It, You Can?t Manage It If You Can?t Manage It, You Can?t Improve It
Targets and Metrics Measuring May Seem Like Extra Work and Too Controlling, but How Else Can You Get a Baseline for Improvement?
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 135
PDCA is the foundation of BPD
PLAN
Annual Business Plan Actions
GMS
100 50
Goals, Objectives, Targets, Methods
DO
Countermeasures
Activities
PROBLEM SOLVING
Regular Reviews
X
Below Expectations Needs Improvement
ACT
GMS Executive Overview
? Open, Team Discussion ? Coaching & Learning ? Get Support & Resources ? Go To See
Meets Expectation
CHECK
John S. Hamalian
Slide 136
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
3rd
1st
0
GMS
Continuous Improvement
Andon Concept
Vision/ Mission
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Values
Health and Safety Priority
Team Concept In-Process Control and Verification
Fixed Period Ordering System/ Order Parts
Simple Process Flow Controlled External Transportation Andon Concept
Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time
Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Quality System Management
Scheduled Shipping / Receiving
Total Productive Maintenance
Business Plan Deployment
Workplace Organization
Internal Pull / Delivery
Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Supply Continuous Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Chain Improvement Tooling and Layout Management Process
Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 137
What is the Andon Concept?
GMS
? The ANDON Concept encourages employees to call for help when there is a problem or out of standard situation, using audio and/or
visual signals to help attract attention ? The ANDON Concept is an enabler to control quality while keeping the process going by pulling in support to address issues before they become problems
Quality Andon System
Hotel “Bell” for Bellhop
Walkie Talkie/Mobile Phone
Airplane Call for Attendant
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 138
Always Remember The Priorities…
GMS
Safety People Quality Responsiveness Cost
Importance
For Example, Sometimes We Have To Sacrifice Quantity to Achieve Quality
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 139
Function of Everyone including Managers and Staff is to Support our Team Members
GMS
Needs help
Team Member
Pull Andon
Team Leader
Support
Decision
Group Leader
Support
Decision
Mgr
Support
Decision
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 140
GMS
Andon Is Not Just a System Of Wires and Lights
It is a Concept of Calling For Help Before It is Too Late
EVERYONE HAS AN “ANDON CORD”
Pull Your Andon!!!
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 141
GMS
Continuous Improvement
Problem Solving
Vision/ Mission
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process
Small Lot Packaging
Values
Simple Process Flow Andon Concept
Health and Safety Priority Product Quality Standards
Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time Workplace Organization
Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Team Concept Period Fixed Ordering System/ Order Parts Quality System Management
Controlled External Transportation
Total Productive Maintenance
Scheduled Shipping / Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Internal Pull / Delivery
Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Supply Continuous Chain Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Improvement Management Tooling and Layout Process
Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 142
GMS
Problem Solving
?
What Is a Problem? A Problem Is Defined As a Discrepancy Between an Existing Standard or Expectation and the Actual Situation
Standard Discrepancy
LEVEL
Actual
TIME
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 143
Create a Company Culture Where “Red” is not Always Bad!
?
? ?
GMS
Problems Are Seeds for Improvement – Don?t Hide them, Let them Rise Up!
Everyone has Problems – the Difference is in how they deal with them! If There Are No Problems, Then Something Is Wrong!
Growing
?No Problem? means Big Problem!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 144
Problem Solving
Blame The Process – Not The People!!!
GMS
Problems Occur Because of Failures in the System
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide
145
Guiding Principles
Everyone is responsible for Problem Solving!
Team Member Team Leader
GMS
Group Leader
Section Leader
Material
Engineer
Manager
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 146
GMS
Practical Problem Solving
Follow-Up & Check
Long-term Countermeasure 6
Problem Description
7
1
2
Problem Definition
5
Root Cause Investigation
4
3 Short-term
Containment
Locate Point of Cause
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 147
Practical Problem Solving Can Be Used For Anything!…
?When
GMS
is Problem Solving appropriate …
- Safety Incident - Significant Customer Dissatisfier - Lost Time Issues - Late Delivery of Good or Service
and any other abnormal situations at anywhere
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 148
Why is Problem Solving Part of Continuous Improvement?
Traditional Companies Stop at Temporary Fixes – They Just Contain the Problem and Put on a Band-Aid
GMS
?
That’s Not Real Improvement – It is Just Getting Back to Standard!
World-Class Companies Find The Root Cause and Put in Steps to Prevent It From Happening Again
GMS Executive Overview
?
Now, THAT is Continuous Improvement!!!
J Hamalian
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 149
Continuous Improvement
Continuous Improvement Process
GMS
Vision/ Mission
Shop Floor Management
People Involvement
Open Communication Process Team Concept
Small Lot Packaging
Values
Health and Safety Priority
Simple Process Flow Andon Concept
Manufacturing Process Validation Management by TAKT Time Workplace Organization
Product Quality Standards
Quality Feedback/ Feedforward
Fixed Period Ordering System/ Order Parts
Controlled External Transportation
Total Productive Maintenance
Internal Pull / Delivery Level Vehicle Order Schedules
Quality Scheduled System Shipping / Management Receiving
Business Plan Deployment
Supply Continuous Chain Lean Design of Facilities, Equipment, Improvement Tooling and Layout Management Process
Problem Solving
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 150
Continuous Improvement Culture
Create an Environment where People are driven to Continuously seek Improvement through the Elimination of Waste
GMS
Set challenging hurdles, conquer them, then raise the bar!!
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 151
Continuous Improvement Culture
When You Climb to the Top . . .
GMS
. . .You Can See the Next Target!
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 152
Continuous Improvement Culture
Improvement Is the Relentless Pursuit of the Elimination of the Enemy - WASTE!!
GMS
Safety
7 Types of
Quality
Waste
Improve
Cost Productivity
Never Be Satisfied With The Status Quo!
GMS Executi
ve Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 153
What is the CIP Method?
1) Grasp the Current Situation 2) Imagine the Ideal Situation – Set Target Make Challenging Targets, Set Expectations – Use BPD
GMS
3) Compare Current Situation to Ideal - See the Gap
4) Define Strategy to Achieve the Ideal 5) Implement CIPs 6) Follow-Up Kaizen/CIP Small Ideas Value Stream Mapping
Ideal
Gap
Suggestion Program
Kaizen/CIP Teams & Workshops
GMS Executive Overview
Go Fast!
Now
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 154
What is the Difference Between Problem Solving and Continuous Improvement Process (CIP)?
Standard
GMS
Problem Solving
Actual
Problem Solving is Getting Back to Standard and Staying There
New Standard
Continuous Improvement Process
Actual (Current Standard)
CIP is Raising The Standard!
J Hamalian
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 155
GMS
Die Change Exercise
GMS Executive Overview
GM Confidential Version Date 2004.8.12
John S. Hamalian
Slide 156
61阅读| 精彩专题| 最新文章| 热门文章| 苏ICP备13036349号-1