一 : 个人简单租房协议
甲方(出租方):_________________身份证:________________
乙方(承租方):_________________身份证:________________
经双方协商一致,甲方将坐落于______________________________房屋出租给乙方XX使用。
一、租房从_____年___月___日起至______年___月___日止。
二、月租金为____元,缴租为____支付一次,人民币(大写)_________元(¥[www.61k.com)____元),
以后应提前___天支付。
三、约定事项
1、乙方正式入住时,应及时的更换房门锁,若发生因门锁问题的意外与甲方无关。因用火不慎或使用不当引起的火灾、电、气灾害等非自然类的灾害所造成一切损失均由乙方负责。
2、乙方无权转租、转借、转卖该房屋,及屋内家具家电,不得擅自改动房屋结构,爱护屋内设施,如有人为原因造成破损丢失应维修完好,否则照价赔偿。并做好防火,防盗,防漏水,和阳台摆放、花盆的安全工作,若造成损失责任自负。
3、乙方必须按时缴纳房租,否则视为乙方违约。协议终止。
4、乙方应遵守居住区内各项规章制度,按时缴纳水、电、气、光纤、电话、物业管理等费用。乙方交保证金________元给甲方,乙方退房时交清水,电,气,光纤和物业管理等费用及屋内设施家具、家电无损坏,下水管道,厕所无堵漏。甲方如数退还保证金。
5、甲方保证该房屋无产权纠纷。如遇拆迁,乙方无条件搬出,已交租金甲方按未满天数退还。
6、备注;_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
四、本合同一式两份,自双方签字之日起生效。另水;_____吨气;____立方电;___度
甲方签章(出租方):乙方签章(承租方):
电话;电话;
______年______月______日
二 : MQTT协议简记
MQTT - MQ Telemetry Transport
消息体

MessageType
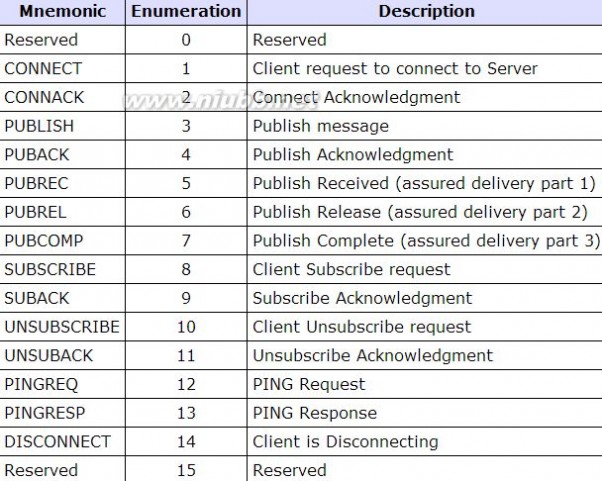
CONNECT
TCP连接建立完毕后,Client向Server发出一个Request。
如果一段时间内接收不到Server的Response,则关闭socket,重新建立一个session连接。
如果一个ClientID已经与服务器连接,则持有同样ClientID的旧有连接必须由服务器关闭后,新建立才能建立。
CONNACK
Server发出Response响应。
0x00 Connection Accepted
0x01 Connection Refused: unacceptable protocol version
0x02 Connection Refused: identifier rejected
0x03 Connection Refused: server unavailable
0x04 Connection Refused: bad user name or password
0x05 Connection Refused: not authorized
PUBLISH 发布消息
Client/Servier均可以进行PUBLISH。
publish message 应该包含一个TopicName(Subject/Channel),即订阅关键词。
关于Topic通配符
/:用来表示层次,比如a/b,a/b/c。
#:表示匹配>=0个层次,比如a/#就匹配a/,a/b,a/b/c。
单独的一个#表示匹配所有。
不允许 a#和a/#/c。
+:表示匹配一个层次,例如a/+匹配a/b,a/c,不匹配a/b/c。
单独的一个+是允许的,a+不允许,a/+/b不允许
PUBACK 发布消息后的确认
QoS=1时,Server向Client发布该确认(Client收到确认后删除),订阅者向Server发布确认。
PUBREC / PUBREL / PUBCOMP
QoS=2时
1. Server->Client发布PUBREC(已收到);
2. Client->Server发布PUBREL(已释放);
3. Server->Client发布PUBCOMP(已完成),Client删除msg;
订阅者也会向Server发布类似过程确认。
PINGREQ / PINGRES 心跳
Client有责任发送KeepAliveTime时长告诉给Server。在一个时长内,发送PINGREQ,Server发送PINGRES确认。
Server在1.5个时长内未收到PINGREQ,就断开连接。
Client在1个时长内未收到PINGRES,断开连接。
一般来说,时长设置为几个分钟。最大18hours,0表示一直未断开。
QoS

QoS=0:最多一次,有可能重复或丢失。
QoS=1:至少一次,有可能重复。
Client[Qos=1,DUP=0/*重复次数*/,MessageId=x] --->PUBLISH--> Server收到后,存储Message,发布,删除,向Client回发PUBACK
Client收到PUBACK后,删除Message;如果未收到PUBACK,设置DUP++,重新发送,Server端重新发布,所以有可能重复发送消息。
QoS=2:只有一次,确保消息只到达一次(用于比较严格的计费系统)。
Clean Session
如果为false(flag=0),Client断开连接后,Server应该保存Client的订阅信息。
如果为true(flag=1),表示Server应该立刻丢弃任何会话状态信息。
Refs
扩展:mqtt协议 / mqtt协议详解 / mqtt协议实现即时通讯
三 : 简单游用户协议
本『软件产品』仅系授权使用,而非贩售版权。[www.61k.com] 1、授权。 『福州天下创世数码有限公司』授权您安装并使用本『软件产品』。 2、限制。 您应保留所有『软件产品』拷贝上之着作权标示。 您不得对本『软件产品』进行反向工程(Reverse engineer)、反向编译(Decompile)或反汇编 (Disassemble)。但若有所适用之法律法规禁止上述限制,则不在此限。 您必须遵守所有『软件』产品使用之相关法律。 3、终止。 若您未能遵守本『许可协议』之条款或条件,则『福州天下创世数码有限公司』得在不妨碍其他权力之情况下,终止本『许可协议』。届时您必须销毁本『软件产品』之所有拷贝。 4、著作权。 凡与本『软件产品』及其拷贝有关之所有权与着作权均属『福州天下创世数码有限公司』或其版权所有者所有。凡与因透过本『软件产品』而存取之资料内容之所有权以及知识产权,均属各该资料之所有权人,并受相关着作权法或其他知识产权法律与条约之保护。本『许可协议』并不授权您就该等资料之内容享有使用之权力。 5、不为瑕疵担保。 您因使用本『软件产品』所造成之任何损失和风险将由您独自承担。在相关法律所允许之最大范围内,『福州天下创世数码有限公司』及其供应商不承担任何瑕疵担保责任与条件,不伦其为明示或默示者,其中包括(但不限于)适售性、适何某特定用途以及不侵害他人权益之默示担保责任。 6、就衍生性损害不负赔偿责任。 在相关法律所允许之最大范围内,『福州天下创世数码有限公司』或其供应商对于您因使用或不能使用本『软件产品』而遭受之特别、衍生性、直接或间接损害(包括,但不限于营业利益之损失、营业中断、数据丢失或其他有形或无形损失)不负任何损害赔赏责任。此项规定不因您事先告知『福州天下创世数码有限公司』或其供应商,该损害发生之可能性而有所不同。 7、其他规定。 本『许可协议』适合中国(香港、澳门、台湾除外)法律。本『许可协议』中未提及到的其他一切权力『福州天下创世数码有限公司』均予保留。若您就本『许可协议』有任何疑问,请接洽『福州天下创世数码有限公司』。网址:http://www.jdyou.com。 8、其他软件。 凡是软件的产品、包装、说明等出现或提到的非福州天下创世数码有限公司所有的软件及名称,其版权属于该产品版权所有者所有,在此向其表示感谢。特别注意: 本『许可协议』所指(试用版『Trial Version』)是『福州天下创世数码有限公司
简单游怎么用 简单游用户协议
』出品的试用版软件产品。[www.61k.com]其功能有限制,并且安装程序、自述文件、或程序本身有明显的中文『试用版』(或『测试版』)或英文『Trial Version』以及具有相同法定含义的文字字样以及未曾注册或不应以任何方式包含、提供注册码,否则就不属于试用版范畴。本软件本版本支持中文域名和通用网址功能,并集成中国互联网络信息中心(CNNIC)的中文上网官方版软件,在安装本软件时同时安装。如果您同意安装本软件和CNNIC中文上网官方版软件,即表明您同时接受中文上网官方版最终用户使用授权协议所有条款。中国互联网络信息中心(CNNIC)中文上网官方版软件最终用户使用授权协议如下:CNNIC中文上网官方版软件最终用户使用授权协议本最终用户软件授权协议(以下简称“协议”)是由您,作为最终用户,与中国互联网络信息中心(以下简称“CNNIC”)共同签订。1. 许可授权按照本协议的以下条款,CNNIC授权您使用本软件及其相关修订、升级或错误更正,该授权为有限、非专用、不可传递、不可转授的,并仅供您在自己的电脑上依照本协议使用。本软件产品为免费软件,用户可以非商业性地下载、安装、复制和散发本软件产品。如果需要进行商业性的销售、复制和散发,例如软件预装和捆绑,必须获得CNNIC的授权和许可。并且,您无权转授本使用许可,不得销售、租借、租赁或散发本软件的拷贝,除非明确获得您、您所在单位或负责人与CNNIC达成的有效书面授权协议。2. 知识产权保护本软件受中华人民共和国著作权法及国际著作权条约、知识产权法、国际版权法及条约的保护,其所有知识产权归CNNIC所有。除非本协议另有明确规定,否则本协议不向您提供任何有关该软件的知识产权。该软件的所有标题和版权,包括但不限于其操作、代码、结构和执行、外观、屏幕显示结果、任何图象、照片、动画、录像、录音、音乐、文字和附加程序(dll、exe等)、随附的帮助材料、及本软件产品的任何副本,均属CNNIC的知识财产。CNNIC保留所有在本协议中未明确授让的权利。用户不得对本软件产品进行反向工程(reverse engineer)、反向编译(decompile)或反汇编(disassemble),违者属于侵权行为,将可能受到来自CNNIC的法律追究,行为人并应当自行承担由此产生的不利后果。3. 有限责任本软件以“现状”方式提供,CNNIC不对该软件作任何明确的、隐含的或法定的保证,包括但不限于任何关于可销售性、特定用途的适用性或不损害第三方利益的隐含保证。CNNIC不对与本软件有着相同或相似实现原理的其它软件(如3721
简单游怎么用 简单游用户协议
网络实名软件等)的冲突做任何明确的、隐含的或法定的保证。[www.61k.com]CNNIC不对您或任何其他人所造成的损失承担责任,这些损失可能来自于与用户安装使用的其他软件的冲突,或由于不能使用本产品而造成的损害,包括(但不限于)直接的、间接的、特殊的、偶然的、惩戒性或结果性的个人损害、商业利润损失、业务中断、信息的丢失或任何其它商业损失。本软件经过详细的测试,但不能保证与所有的软硬件系统完全兼容。如果出现不兼容的情况,用户可拨打电话、Email、传真等方式将情况报告CNNIC,获得技术支持。4. 软件认定本软件产品可以通过网络等途径下载、传播,对于从非CNNIC指定站点下载的本软件产品以及从非CNNIC发行的介质上获得的本软件产品,CNNIC无法保证该软件的完整性、安全性和有效性,不承担由此引起的直接和间接损害责任。5. 功能升级CNNIC保证本软件的升级模块中也不含有任何旨在破坏用户计算机数据和获取用户隐私信息的恶意代码,不含有任何跟踪、监视用户计算机和或操作行为的功能代码,不会监控用户网上、网下的行为或泄漏用户隐私。6. 自愿性软件和卸载权本软件为自愿性质的软件,在Windows操作系统启动时自动运行,您可以在任何时候利用Windows的添加/删除程序功能来卸载本软件,因删除产生的一切后果由用户承担。由于本软件与某些浏览器插件软件(如3721网络实名等插件)不兼容,这些插件将导致本软件功能无法正常使用。为了确保本软件功能有效,本软件安装后将覆盖或卸载这些插件。同时本软件安装后用户也将有可能无法下载、安装这些与本软件不兼容的插件软件。如果用户确需安装这些插件,请先从系统“控制面版”的“添加/删除程序”中卸载本软件。7. 终止如果您违反了本协议,则您使用本软件的授权将被终止。终止后,您必须将本软件的拷贝及所有相关文档销毁。8. 争议解决双方一致同意本协议的内容及效力,双方一致同意由于执行本协议而产生的一切纠纷适用中华人民共和国法律,并由CNNIC所在地法院管辖。9. 通过下载安装或者对弹出插件窗口点击“是”安装软件包,表明您已同意本协议,并且作为本协议的一方而受其约束。如果您不同意本协议的所有条款,请不要下载或安装本软件,或者对弹出插件窗口点击“否”。中国互联网络信息中心(CNNIC)2003年9月
四 : HDCP协议简介
HDCP: what it is and how to use it
什麼是HDCP?如何去運用?
Whether or not you believe in content protection, if you design digital-video products, you must deal with the technology. Here's what you need to know to start applying high-bandwidth digital-content protection.
無論你是否相信,在設計數字視頻產品時,你一定得處理HDCP技術。而開始應用高帶寬數字內容保護(HDCP)是需要去了解的。
By Jim Lyle, Silicon Image Inc -- EDN , 4/18/2002
The DVI (digital visual interface) delivers video images with very high resolution and essentially perfect quality. Although this capability is a boon to end users, it has sparked great concern in the entertainment industry, because it raises the specter of unauthorized mass duplication and distribution of "perfect" copies of Hollywood's most valuable content.
DVI(數字視頻接口)傳輸的畫面解析度很高而且畫面本身的效果也很完美。盡管這種功能給終端用戶帶來了實惠,但是由於 這種技術成為各種盜版的克星,它在娛樂界引起了極大的關注。
Traditional copyright protections (such as infringement lawsuits) are suitable only in specific cases and are impractical on a mass scale. They would be entirely useless against the millions of people who might buy DVDs and copy them for their friends and relatives. Therefore, much of the consumer-electronics equipment available today incorporates
copy-protection mechanisms. Different types of devices use different kinds of copy protection. Most techniques stem from cooperation between content providers and equipment manufacturers. For DVI, such a cooperative effort has produced a mechanism called HDCP (high-bandwidth digital-content protection), a two-part cryptographic method to control video delivery.
傳統的版權保護(諸如侵權訴訟)僅僅適用與特定的案例,而對於大多數而言是不切實際的。對那些數以百萬可能買DVD或拷貝DVD內容給他們的親人或朋友的人來說,傳統的版權保護可能完全起不到作用。因此,目前大量的可買得到的消費電子設備包含了版權保護功能。不同類型的裝置使用不同種類的版權保護。大部分技術源與內容供應商與設備制造商的合作。對於DVI這種合作的成果已經產生一個稱之為HDCP(高帶寬數字內容保護)的技術。它是一個用密碼寫的工具並用與控制視頻傳輸。
What HDCP is—and isn't
HDCP是什麼?又不是什麼?
HDCP is content protection, not copy protection (or more accurately, copy restriction). The difference is subtle but very important. HDCP is not designed to prevent copying or recording, nor will it do away with "time-shifting" (taping of TV
programs to pause live video or to enable you to view programs later). The ability to do these things has revolutionized TV viewing. People want these features, and the capabilities will only improve.
HDCP是內容保護而不是拷貝保護(或更準確地講,拷貝限制)。這些區別不但微妙而且非常重要。HDCP不是防止拷貝 或錄影而設計的,也不是為消除"time-shifting"(停止現場的視頻節目而對它進行錄影,使你能夠在晚些時候能觀看它)而設計的。TV在做些事情的功能上已經實現了突破性的大變革。人們想要的這些特點和功能將改善。
Yet, as these features become more capable and ubiquitous, protecting copyrighted material becomes increasingly difficult. The copyrights are important; they protect both those who create materials and those who use them. The Internet raises the stakes because it enables unwitting or unscrupulous low-cost mass distribution of copyrighted material.
可是,由於這些特色變得越來越有用而且無處不在,保護那些受到版權保護的資料變得越來越困難。版權是重要的,它既保護那些創造資料的人又保護了那些使用這些資料的人。而因特網會因那些不知情的或不講道德的人銷售大量廉價的版權資料而引起了風險。
Your home-theater system can implement any kind of copy protection it needs. It might allow unrestricted copies, a limited number of copies, limited use of copies, or no copies at all. The exact mechanism depends on the source material, how it is distributed, and the equipment design and configuration. It is important, however, that the designer's decisions on the
permissible extent of copying be final.
你的家庭影院系統能夠實現任何一種類型的拷貝,而這種類型是的它所需要的。它可能不受限制的拷貝,或有限的拷貝數量,或有限的拷貝使用,甚至根本就不允許拷貝。準確的途徑取決與資料的源頭,它最終可被拷貝的程度有多少。
At this point, HDCP enters the picture. The DVI connection it guards is usually the last link in the video chain. The system's intelligence typically lies somewhere upstream, for example, in the satellite-TV or cable box. Such locations are the right places to decide on copy-protection strategies. HDCP merely protects the choice.
基於此HDCP進入圖片領域.DVI所保護的連接常常連接在視頻電路裡。系統的典型能力在與某些地方,如衛星電視、有線電視盒的上行數據。這些指定的位置是決定拷貝保護策略的好地方。而HDCP隻不過是保護那些被選中的內容。 System architecture
系統結構
A DVI link is a point-to-point connection with a single transmitter and receiver, so the simplest HDCP system resembles the one that Figure 1 shows. The host is a PC, a set-top box, a DVD player, or a similar video source that contains the DVI transmitter and a set of HDCP keys. The display is a monitor, flat-panel television, or projector that contains the DVI receiver and a (different) set of HDCP keys.
DVI連接是信號傳送器和接受器之間點到點的連接。因此最簡單的HDCP系統猶如圖一所示。主機可以是PC,或機頂盒,或DVD播放機,或類似的包含DVI傳送器和一套有HDCP密碼的視頻設備。顯示設備可以是顯示器,或帄板電視,或包含DVI接受器和一套(不同的)有HDCP密碼的投影機。
By design, the HDCP protocol couples a single transmitter to a single receiver. Other devices can't eavesdrop. In some cases, though, the system may need more than one host or display device. One example is a computer that has
connections to both a monitor and a projector. Also, many home-theater systems use an AV receiver to route audio and video signals among a variety of inputs and outputs (Figure 2).
通過設計,HDCP協議將信號傳送器和信號接收器連接在一起而使其他的設備不能從中竊取信息。雖然在某些情況下,系統可能需要的不止一台主機或顯示設備。計算機就是一個例子,它既連接顯示器,又連接著投影機(或放映設備)。再如,許多家庭影院系統都使用AV接收器沿預定的線路再各種輸入,輸出端口間傳輸音頻信號和視頻信號。(見圖二)
The HDCP specification defines a repeater function to accommodate configurations such as the one that Figure 2 shows.
A repeater is an active device that has one or more DVI/HDCP inputs and one or more DVI/HDCP outputs. Figure 3 shows another repeater example. The two outputs and one input represent the PC/monitor/projector example. On one side, the repeater acts as a receiver, accepting video from upstream. On the other side, the repeater acts as a transmitter, sending the video downstream.
HDCP規格定義了一個中繼功能,它用於存放如圖2顯示的結構配置。中繼器是一個有效的設備,它有一個或多個DVI/HDCP輸入和輸出。圖3顯示的是另一種中繼器的例子。兩個輸出和一個輸入表示PC,顯示器,或投影機。一方面,中繼器扮演接收器的角色,接收來自上行數據的視頻信號;另一方面,它又有傳送器的作用,發送下行數據流的視頻信號。
Each of these links is separate. Each has a unique transmitter and receiver, and from an HDCP perspective, the data on each is encrypted in a unique way (which is a function of the keys for that particular link). Though separate, the links are not entirely independent: Certain HDCP functions must gather status and other information about the entire system, so the HDCP specification defines how to propagate this information upward through repeaters.
這些連接(鏈路)彼此是分開的。從HDCP的角度看,每一個連接(鏈路)都有唯一的傳送器和接收器。並且在每一個連接(鏈路)上的數據都經過獨一無二的方式加密處理。(對於特定的連接(鏈路),這種方式起到很重要的作用)
Note that hosts must support repeaters. The specification requires this support, and your customers will need the flexibility.
A system can also include more than one repeater. Indeed, there may be as many as seven levels of repeaters and 127 receivers. (Repeaters count toward this limit.)
但是要注意,主機必須支持中繼器。而且規格也要求這種支持,因為客戶也要求這種靈活性。一個系統可能不止一個中繼器。
事實上,系統可以包含七層中繼器和127個接收器。(這個中繼器的數目接近極限)
Authentication and revocation
驗証和廢止
You cannot confidently use HDCP unless both the transmitter and receiver support it and work properly. Authentication tests and verifies these functions and, if unsuccessful, blocks transmission. Authentication must exclude devices that have been compromised or hacked. Revocation accomplishes this exclusion.
除非傳送器和接收器能支持HDCP,並且保証它能正確地工作,否則你將不能放心地使用HDCP。如果HDCP不能正常工作,則需要驗証並測詴這些功能和傳輸模塊。鑒定証明必須排除那些陳腐破舊或是容易危及安全的設備並取消完成這種被排除在外的現象。
First, transmitters and receivers must demonstrate knowledge of a valid set of keys. The keys themselves are kept private and never revealed, but each side of the link calculates a mathematical result, R0, which depends on the key values. This calculation also initializes the cipher engines with a secret value, KS, which forms the video-encryption key.
首先,傳輸器和接收器顯示一套有效的按鍵的消息。按鍵本身必須是獨立的決不能相互影響,而在連接的兩邊要計算出一個數學結果—R0,它取決於按鍵值。這種計算也用一個隱藏的值—KS初始化引擎密碼.而該隱藏值也就構成了視頻加密的關鍵。 The transmitter generates a pseudorandom number, AN, which it sends to the receiver along with the transmitter's KSV (key-selection vector). The receiver then sends its KSV to the transmitter. The KSV values must have the right form—they must contain exactly 20 ones and 20 zeros. If they do, each of the cipher engines independently calculates the R0 and KS results.
傳送器產生一個偽隨機數字,此數字沿傳送器的KSV(重要選擇路徑航向)發送到接收器.然後接收器將其KVS反饋回傳送器。KVS值必須有正確的形式,他們必須嚴格地包含20個1和20個0。如果他們做的話,每一個密碼引擎獨立地計算R0和KS結果。
Finally, the system compares the R0 values that the transmitter and receiver generate by the transmitter and receiver. The mathematical function prevents the transmitter keys from working in a receiver and the receiver keys from working in a transmitter. Matching R0 values strongly suggest valid keys.
最後,系統對由傳送器和接收器產生的R0值進行比較。數學上的功能保護來自工作在接收器中的傳送密碼和工作在傳送器中的接收密碼。相匹配的R0值強有力地暗示有效的密碼。
The flowchart in Figure 4 shows an example of the firmware operations needed to manage the computation process. This example assumes that the transmitter is Silicon Image's (http://www.61k.com) SiI168 device, but any HDCP transmitter performs similar functions.
圖4中的流程圖顯示的是軟體操作需要去處理計算過程的例子。這個例子假定傳送器為硅畫面的SiI168設備,而任何HDCP傳送器都可以實現類似的功能。
Even valid keys can become compromised (hacked), so HDCP includes a mechanism to revoke keys. The KSV values are unique to each key set and, therefore, to each device. The system can then compare these values to a revocation list, and if either the transmitter or receiver appears on that list, authentication fails. Updates to the revocation list arrive with new media and are automatically integrated. So if a key set somehow does get exposed or copied, the damage can be limited. 即使有效的密碼可能外泄,HDCP還包括一個機構裝置可以廢除這個密碼。因此,對於每一個所設定的密碼和每一個設備,KSV值是唯一對應的。然後系統將這些值與廢除清單比較,如果傳送器或接收器中的值在這份清單中,那麼驗証失敗。更新送來的廢止清單和新的媒介會自動地結合在一起。所以,如果由於某種未知的原因而導致設置的密碼外泄或被復制,這種危險能得到限制。
This revocation process does not affect other devices, even if the devices are of the same make and model. In that sense, KSV values are like serial numbers. Suppose that Sally and Bob buy the same kind of TV on the same day at the same store. Bob somehow hack s his set, gets caught, and has his KSV value revoked. Sally needn't worry. Her TV has a different KSV value and won't be affected in any way.
這種廢止過程不影響別的設備,即便這些設備是相同的型號。在這種情況下,KSV值就好比序列號。假如Sally 和 Bob同一天在同一家商店購買相同款式的電視。由於某種不知的原因,Bob出租了他的電視而且要回這台電視也比較為難,他就廢止了他的KSV值。此時Sally就無須擔心了因為他的電視有一個與Bob不同的KSV值。
Upstream authentication
Even if valid hardware and valid keys are present, it might still be possible for an external agent (typically a driver or software application) to interfere. In the worst case, this agent could make it appear that the HDCP hardware is present and active when, in fact, it's not there, not working, or altered in some way. Upstream authentication enables the system to prevent or detect this kind of problem and can also permit the system to move confidential values from the hardware to the software application without fear of the values being observed or altered.
即便有效的硬件和有效的密碼是不易忘記的,但是仍舊存在外部原因(如:驅動或應用軟件)幹擾的可能。最糟糕的情況是,實際上沒有HDCP硬件或HDCP硬件沒有工作,而由於外部原因使它看起來在工作或一些方面在改變。上行數據驗証確保系統能防止或偵測到這類問題,也能讓系統將機密數據從硬件移到應用軟件而不需擔心這些數據被別人看到或改變。 The simplest form of upstream authentication uses purely physical barriers. Many applications have fixed hardware and firmware configurations and are not subject to user-installed upgrades or modifications. The absence of such modifications is typical of consumer-electronics products, including devices such as set-top boxes and DVD players. In such cases, the required security can be established by design, verified by test, and protected by the enclosure and the requisite "no user-serviceable parts" warning label.
最簡單的上行數據驗証形式是使用純物理屏障。許多引用固化在硬件和軟體架構中應用,並不易受到用戶安裝升級或修改設置的影響。這類缺少修改的設置是一種典型的電子消費產品,這類設備包括機頂盒和DVD播放機。在這種情況下,被要求的安全性可以通過設計來建立,通過測詴來証實,還可以通過附貼必要的’’用戶禁用’’警告標簽來保護。
A personal computer is completely different, though. Users frequently install their own software and can download new drivers or plug-ins with just a few mouse-clicks. In this environment, upstream authentication combines hardware and software protocols that include encryption and signature algorithms, with the implicit assumption that no driver is
trustworthy. Special cryptographic messages that only the software can interpret hide link status and confidential data values. The drivers can only pass the messages along. If the drivers fail to forward the messages or tamper with them in any way, the mischief will be detected.
然而,個人電腦是完全不同的。用戶常常安裝他們自己的需要的軟件或點幾下鼠標下載新的驅動。在這種情況下,上行數據驗証含蓄地假定驅動是不值得信任的,並將硬件和包含加密和特征演算法的軟件協議聯合在一起。隻有用特定的軟件才能解開,專用的用密碼寫的消息,隱藏著連接狀態和機密數據值。而驅動隻能向前傳遞消息。如果傳遞失敗或消息被破壞,那麼這種破壞根源將被偵測到。
The original HDCP specification does not define upstream authentication, as it is application-dependent and isn't always necessary. A companion specification defines a recommended implementation for PC applications, however. This
specification uses a mathematical system that is similar to HDCP's downstream side. The keys come from a different key space, though, and will not interoperate with the downstream keys. The specification defines only a limited number of functions. These functions include Status Read (verifies that the HDCP link is working properly), Read M (transfers the confidential M0 value, which the software application needs), and Read Z (transfers ZK, which provides initial keying material in some cases).
由於上行數據驗証是個獨立的應用,且它並非必不可少,所以最初的HDCP規格沒有定義上行數據驗証。對於PC應用,手冊規格定義了一個推薦的執行方法。然而,這個規格使用了一個類似HDCP的下行數據邊的數學系統。密碼來自不同的密碼空間,可是它們不能用下行數據密碼相互操作。規格隻定義了有限的函數。這些函數包括’’讀狀態’’(証實HDCP連接正常),’’讀M” (轉移機密M0值,這個值是軟件應用需要的),’’讀Z” (轉移ZK,在某些情況下它提供最初的密碼資料)。
Encryption
加密
Encryption, of course, is the brick and mortar of the HDCP strategy, and it prevents eavesdropping. The encryption alters the video data using a reversible function (which XORs the data with the cipher-engine output). Each pixel is separately altered, producing a video image that is thoroughly scrambled and has no recognizable features. If the transmitter and receiver are properly synchronized, the XOR functions cancel, properly reproducing the original video.
當然,加密是HDCP策略的防護堡壘,它能防止偷聽。加密用可逆功能(XOR輸出密碼引擎數據)改變視頻數據。每一相素交替改變,產生完全沒有規律,沒有可識別特征的視頻圖象。如果傳送器和接收器同步正常,那麼取消XOR函數也能正確地從現原始圖象。
During encryption, a link-integrity check occurs approximately every two seconds. Every 128 frames, the receiver and transmitter generate a new value, RI, which is similar to the original R0. Comparing these values verifies that the link
remains synchronized. This check serves three main purposes. First, it provides additional verification that the initial states were a proper match. Second, it provides ongoing feedback that the link is working properly. Finally, it narrows the window for an outside agent to disrupt the link.
加密期間, 差不多每兩秒就進行一次完整的鏈路檢查。每隔128禎接收器和傳送器就產生一個新的值R1,它與初始值R0非常類似。通過比較這些值來証實鏈路是保持同步的。這種檢查動作有三個目的。首先,它提供了額外的檢驗表明初始狀態匹配正常;第二,它提供連續的反饋表明鏈路工作正常;最後,它可以減少外界因素對鏈路的影響。
Design considerations and pitfalls
設計考慮及易犯的錯誤
Product designers frequently ask when they will need to be ready for HDCP. The trite-but-true answer—the sooner the better—raises a chicken-and-egg quandary, however. Nobody wants to go to the time, trouble, and cost of building a DVI/HDCP interface into a product if customers can't use it. The market needs both PCs and monitors (or set-top boxes and TVs) before this feature can become effective.
產品設計者經常問什麼時候需要準備好HDCP功能。一個帄庸但真實的回答是越快越好。然而這就引起了一點小困惑。如果客戶不使用 HDCP功能,沒有人想為將DVI/HDCP接口加到產品中而引起時間,精力,成本上的麻煩。在這種功能成為有效之前,市場需要的是個人電腦和顯示器(或機頂盒和電視)。
A look at the other side of the coin is important, though. Although having a feature that you don't need isn't good, needing a feature that you don't have can be worse. High-definition, digital-quality, premium video is coming but only to products built with security in mind. Designers who delay implementation risk ignoring their customers' needs.
但是,事情的另一面也同樣重要。雖然有一個你不需要的功能在你的產品中不是太好,但是在產品中有一個你不要的功能則是一件糟糕的事。高清晰,數碼,優質畫面的產品即將出現,但對於產品安全的建立還隻是一種構思。冒險延後實行這種設計的設計者忽略了客戶的要求。
The good news is that quite a few HDCP-enabled products (both host and display) are either in production or soon will be. Leading manufacturers and content providers have already announced support for DVI/HDCP, and many more will do so in the coming months. So the question is not so much whether you should do this now. It's whether you're already too late. 一個好消息是:相當多的有HDCP功能的產品(主機和顯示設備)或在生產中或即將生產。主要的制造商和內容提供商已經宣布支持DVI/HDCP功能,並且很多商家在未來的一段時間內將這麼做。所以說,問題不在與你是否應現在應該這樣做,而是你已經做得太晚。
One special consideration: Television sets are a big investment (some bigger than others), and people tend to hold on to them for a long time. It's doubly important to future-proof these products.
一個特別的考慮:電視機是一筆大投資(相對其他的要大),所以人們常常延誤很長一段時間。對於這些不會過時的技術的產品而言,就顯得更加重要。
Adding HDCP to a product
增加HDCP功能到產品中
To add HDCP capabilities to your product, you need a few basics. First, you need the DVI: a connector, the DVI silicon, and a small number of discrete components. Then you need the HDCP function, which is generally integrated into the DVI
silicon. You also need the HDCP keys and some kind of nonvolatile memory to store them. (The exact kind depends on the HDCP function, but in some cases, the memory also resides in the DVI silicon.)
要增加HDCP功能到產品中必須具備幾個基本條件。首先,你要有DVI:一個連接頭,DVI矽和一些獨立的元件。其次,產品需要有HDCP功能,這個功能通常被集成在DVI矽裡。同時也需要HDCP密碼和穩定的內存來存儲。(精確度取決於HDCP功能,但在某些情況下,內存也屬於DVI矽。
For example, suppose a monitor or TV manufacturer wants to add an HDCP-capable DVI to an analog product line. Figure 5 highlights (in red) the necessary new elements. The essential chassis remains the same. One of the analog inputs merely changes to digital. The alterations are isolated, and the manufacturer might even implement them as a daughter card or optional feature.
比如:假設一台顯示器或電視制造商希望增加含HDCP功能DVI到模擬產品中。如圖5 (紅色部分)強調了必要的新元件。必要的底座是同以前一樣的。其中一個模擬輸入僅僅變為數字輸入。這種變化是獨立的,有些制造商甚至已經將他們作為可供選擇的功能而這樣做了。
The additional circuitry is not complicated; Figure 6 details one example. The primary elements are the DVI connector
(CONN1), the SiI905 HDCP-monitor controller, and an EEPROM. The SiI905 contains all of the DVI and HDCP circuits and produces an RGB analog output. The function is essentially self-contained and requires no external firmware or control. Other varieties of interfaces are also available, including some with digital outputs and some with advanced features, such as scaling and on-screen displays.
增加的電路並不復雜,圖六給出了細節。最主要的元件是DVI連接頭(con1), SiI905 HDCP-monitor控制器 和EEPROM。SiI905包含全部的DVI和 HDCP電路,並產生RGB模擬輸出。這種功能是必須自帶的無須額外的軟件或控制。其他種類的接口的使用也是必須的,包括一些數字輸出和具有縮放和on-screen顯示的高級特色功能.
Adding an HDCP-capable DVI output to a product such as a graphics adapter or set-top box is a similar exercise. You still need to add the interface silicon, the nonvolatile key memory, and the DVI connector. The circuit complexity is similar to that shown for the receiver. In general, though, the output-side components are not self-contained. HDCP hosts must control the interface and the information exchange. This requirement typically adds software or firmware. The functions aren't complex, but they do add to the development and test effort.
Don't forget that HDCP hosts must also support repeaters. In practice, then, the software or firmware probably has to
collect the KSV list and verify its digital signature. HDCP hosts must also solve the upstream-authentication problem, either by explicitly incorporating authentication or, perhaps, by using an architecture that prevents end users from making substantial additions or modifications.
Licenses, compliance, and robustness
Every manufacturer seeking to build an HDCP product must obtain a license that allows use of the technology and purchase of the requisite keys. In addition, the license sets forth a set of compliance and robustness.
The compliance rules ensure that HDCP products work together, even among different product types and manufacturers. They also limit the permissible types of configurations and place specific restrictions on video copying, buffering, and available outputs. For example, HDCP products may not make copies but are allowed to temporarily buffer video for specified purposes. HDCP products must use unique keys, too, and are not allowed to have decrypted digital or analog outputs.
The robustness rules make it difficult to circumvent the HDCP technology. In other words, an HDCP product must suitably protect its secrets and must not include switches, jumpers, or simple hardware modifications that trivially bypass some of the intended restrictions.
The important point is that, ultimately, each OEM must ensure that its products are both secure and compliant. The
interface-silicon manufacturer can help, however, and, indeed, helping is a good way for an IC supplier to add value to its products. In the final analysis, though, equipment manufacturers that integrate all of the HDCP elements must ensure that the final product is compliant and robust.
So what must a product designer do? First, get a copy of the license and study it. (You can find it at the Digital Content Protection, LLC Web site, http://www.digital-cp.com/.) In particular, Exhibit D-1 contains a checklist that asks a series of questions that, in effect, spell out the requirements in exhaustive detail. Second, make sure that your product adequately protects the keys. This protection is critical, and many of the rules are intended to ensure the keys' security. Sometimes, meeting this requirement will require special packaging or encapsulation. Also, pay attention to any manufacturing process that includes the keys. Protecting the keys in the final product is not enough; it's also important to protect them at every stage of design, manufacturing, and test. Find out how the keys are first received and decoded, when and where are they programmed, and whether subcontractors are involved. Find out whether inventories need special protection. Find out the answers to all of these questions and more. This requirement need not be daunting, nor must the process be burdensome. Nevertheless, compliance will be easier and cheaper if you think through the issues in advance.
Compatibility testing
兼容性測詴
You can ensure compatibility among products from different vendors only if all meet some suitable level of specification compliance. Currently, however, no lab or service tests the compliance of HDCP products. Manufacturers need this service, and ongoing discussions aim to establish it. In the meantime, plug fests fill the void.
隻有來自不同商家的產品都與規格承諾的內容相一致時,你才能確保你的產品的兼容性。然而,當前還沒有一家實驗室或服務機構為HDCP產品來做這樣的事情。制造商家需要這樣的機構並願為建立這樣的機構而繼續商討。與此同時,plug fests填補這項空白。
A plugfest is an increasingly common gathering at which many vendors (including competitors) test their products. Such testing can only indirectly verify a product's compliance, but it does provide good feedback on the product's compatibility. Plugfests are not really conducive to in-depth analysis, because test equipment and test time can be scarce and also
because competitors are often hesitant to reveal details or quirks. Still, the events are usually helpful and result in improved interoperability.
插拔測詴法(??)是很多廠商(包括競爭商)用來測詴他們的產品的一種越來越普遍的測詴方法。這種測詴隻能間接地驗証產品的性能參數是否與規格相符,但是同時它又對產品的兼容性提供了一個好的反饋信息。 由於不具備測詴設備和時間等條件,且競爭對手又不願展示產品的技術細節和改變,所以插拔測詴法(??)並不能進行深度的分析。盡管如此,這個項目還是比較有用的,並能讓軟硬體在多種品牌機器上能有意義的溝通。
For an HDCP product, compatibility testing divides into two equally important parts. The first part concerns the underlying DVI-transport protocol. If the protocol is unreliable or incompatible, no other testing matters. Subtle glitches can cause catastrophic HDCP-link failures, so exhaustive testing of the link's reliability is imperative. Tests must span a wide frequency range and use different voltages and jitter levels.
對於一個HDCP產品,兼容性測詴分為兩個同樣重要的部分。第一部分關於基本的DVI傳輸協議。如果協議是不可靠的或不相容的,那麼就沒有別的測詴問題。細微的小毛病都可能導致災難性的HDCP連接故障發生.因此連接的可靠性的詳盡測詴是極為重要的。測詴必須間隔一定的時間范圍並使用不同電壓,測量波動的程度。
HDCP testing includes both authentication and encryption phases. Plugfest testing usually uses the public keys published in the HDCP specification. If possible, repeat this testing at different resolutions and frequencies and with different cables and configurations. Let the test run for a while; glitches that can break the link or confuse the logic may not occur for
several minutes. Try unusual operations, too. Change the channel, reauthenticate while the link is active, and do anything else you can think of to expose system quirks.
HDCP測詴既包括驗証階段又包括加密階段。Plugfest測詴常常使用出版在HDCP規格中的共用密碼。如果可能,可用不同的電纜線和配置在不同的解析度和頻率條件下重復這個測詴。讓測詴進行一會,確保在幾分鐘的時間裡能導致連接中斷或邏輯混淆的技術故障不會發生。同時也可以嘗詴異常操作。當處於連接中的時候,改變通道從新驗証,嘗詴任何一個你能想到的方法去揭露系統的突然轉變。
If you are testing a host device that serves as the link master, you need to provide the test software that drives the entire authentication process. Make the software flexible. Include the ability to override values, such as An; change device addresses and modes; and dump and alter registers. If at all possible, bring the source code, a compiler, and the program's author.
如果你想測詴一台作為鏈路核心的主機設備,那麼你需要提供驅動整個驗証過程的測詴軟件。確保軟件靈活可靠,包括1.可以使值,如An無效的功能;2.改變地址和模式;3.轉儲和改變寄存器。如果可能的話,帶上源代碼,編譯器和軟件設計者。
If you are testing a display device, you can rely on the other guy to provide the link-control software. Receivers are slaves that use standardized register maps. However, if the receiver incorporates firmware, all of the previous comments about the host software apply. Come prepared to change the software and to examine variables and registers.
The real challenge at these events is to find a way to be as helpful as possible within the constraints of the competitive environment. A thorough test-and-debug session sometimes requires disclosure of details that one side really doesn't want to share with the other. Such sessions also involve risk, because design flaws can surface while competitors are watching. Still, the benefits are enormous if you can get past these concerns and concentrate on the test at hand. Take copious notes, especially of unexplained behaviors and phenomena. Follow up on them too, either at the event or back at the office.
The best time to find bugs, of course, is before they get designed in. Toward this end, carefully read the specification. Don't forget the errata or the license, either, because they contain additional clarifications and restrictions.
Future directions
As it is currently defined, DVI 1.0 is specified solely for connection between a computer and a monitor. (The present DVI license contains language to that effect.) That situation is changing, however, as more consumer-electronics devices incorporate DVIs.
DVI and HDCP are evolving in subtle ways to meet the needs of this new marketplace. You can see the changes in smaller connectors, longer and lower cost cables, audio support, and alternate color spaces. The licenses and the specifications will be updated accordingly, and the result may have a new name to differentiate it from the existing DVI and HDCP interfaces. Backward compatibility is a top priority, though, so that today's designs don't become obsolete tomorrow.
The DVI 1.0 interface provides premium-quality performance. With the addition of HDCP technology, it constitutes the
preferred means of delivering copyrighted high-bandwidth material. If you're a manufacturer, you should start thinking now about adding DVI to your products. The design is not difficult, and it will ensure that your products can ride the coming wave of high-definition content and services.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Author Information
Jim Lyle is a senior staff engineer at Silicon Image, where he has focused on the system architecture and integration of the company's DVI and HDCP products. He holds a degree in electrical engineering from the University of California at Berkeley and has worked at Tandem Computers, Sun Microsystems, and National Semiconductor. His other interests include antique radios and Scottish country dancing.
五 : 个人简单租房协议
甲方(出租方):_________________身份证:________________
乙方(承租方):_________________身份证:________________
经双方协商一致,甲方将坐落于______________________________房屋出租给乙方XX使用。
一、租房从_____年___月___日起至______年___月___日止。
二、月租金为____元,缴租为____支付一次,人民币(大写)_________元(¥____元),
以后应提前___天支付。
三、约定事项
1、乙方正式入住时,应及时的更换房门锁,若发生因门锁问题的意外与甲方无关。因用火不慎或使用不当引起的火灾、电、气灾害等非自然类的灾害所造成一切损失均由乙方负责。
2、乙方无权转租、转借、转卖该房屋,及屋内家具家电,不得擅自改动房屋结构,爱护屋内设施,如有人为原因造成破损丢失应维修完好,否则照价赔偿。并做好防火,防盗,防漏水,和阳台摆放、花盆的安全工作,若造成损失责任自负。
3、乙方必须按时缴纳房租,否则视为乙方违约。协议终止。
4、乙方应遵守居住区内各项规章制度,按时缴纳水、电、气、光纤、电话、物业管理等费用。乙方交保证金________元给甲方,乙方退房时交清水,电,气,光纤和物业管理等费用及屋内设施家具、家电无损坏,下水管道,厕所无堵漏。甲方如数退还保证金。
5、甲方保证该房屋无产权纠纷。如遇拆迁,乙方无条件搬出,已交租金甲方按未满天数退还。
6、备注;_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
四、本合同一式两份,自双方签字之日起生效。另水;_____吨气;____立方电;___度
甲方签章(出租方):乙方签章(承租方):
电话;电话;
______年______月______日
本文标题:简单租房协议-个人简单租房协议61阅读| 精彩专题| 最新文章| 热门文章| 苏ICP备13036349号-1