一 : 在Linux系统上使用转发服务器处理邮件通信的教程
当你启动并运行应用服务器后,你就需要一台好的邮件服务器来为你传递邮件。我为我所有的服务器开通了postfix邮件服务,下面就是我常用的配置。
CentOS 6上安装Postfix
yum install postfix
默认安装了Sendmail,所以最好将它停掉并移除。
service sendmail stop
yum remove sendmail
Postfix包含了两个配置文件main.cf和master.cf,对于基本的配置,你需要修改main.cf。同时,postfix可以像shell变量一样定义参数,并通过$来调用。这些参数不需要再使用前定义,Postfix只在运行中需要时才会查询某个参数。
配置postfix
vim /etc/postfix/main.cf
去掉以下行的注释
# 你的主机名
myhostname = yourhostname.com
# 你的发件域
myorigin = $myhostname
# 指定用于接收邮件的网络接口,这里指定 localhost 是因为我们只用来接受本地的程序投递
inet_interfaces = localhost
# 指定所使用的协议,可以使用“all”来增加 IPv6 支持
inet_protocols = ipv4
# 指定所接受的邮件域
mydestination = $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain, localhost
# 仅转发本地主机的邮件,而不是主机所在的网络
mynetworks_style = host
启动postfix
service postfix start
这些基本的postfix配置可以让你的机器发送邮件,你可以通过发送邮件并检查“maillog”日志文件来验证。
echo test mail | mail -s "test" leo@techarena51.com && sudo tail -f /var/log/maillog
# 输出的日志类似如下
Aug 25 14:16:21 vps postfix/smtp[32622]: E6A372DC065D: to=, relay=smtp.mailserver.org[50.56.21.176], delay=0.8, delays=0.1/0/0.43/0.27, dsn=2.0.0, status=sent (250 Great success)
Aug 25 14:16:21 vps postfix/qmgr[5355]: E6A372DC065D: removed
但是,上述配置并不够,因为邮件服务大多数时候都会被垃圾邮件挤满,你需要添加SPF、PTR和DKIM记录。即便如此,你的邮件仍然可能被当作垃圾邮件来投递,因为你的IP地址被列入了黑名单,大多数时候是因为你的vps先前被入侵了。
还有另外一种选择,或者说是更好的方式是使用第三方邮件提供商提供的邮件服务,如Gmail,或者甚至是Mailgun。我使用Mailgun,因为它们提供了每个月10000封免费电子邮件,而Gmail则提供了每天100封左右的邮件。
在“/etc/postfix/main.cf”中,你需要添加“smtp.mailgun.com”作为你的“转发主机”,并启用“SASL”验证,这样postfix就可以连接并验证到远程Mailgun服务器。
添加或取消以下行的注释。
relayhost = [smtp.mailgun.org]
smtp_sasl_auth_enable = yes
smtp_sasl_password_maps=static:your_username:your_password
smtp_sasl_security_options=noanonymous
Postfix本身不会实施“SASL”验证,因此你需要安装“cyrus-sasl-plain”。
sudo yum install cyrus-sasl-plain
如果你不安装此包,那么你就会收到这条错误信息“SASL authentication failed; cannot authenticate to server smtp.mailgun.org[50.56.21.176]: no mechanism available)”
重启postfix
sudo service postfix restart
使用TLS加固Postfix安全
Postfix支持TLS,它是SSL的后继者,允许你使用基于密钥的验证来加密数据。我推荐你阅读 ,以了解TLS是怎么和postfix一起工作的。
为了使用TLS,你需要生成一个私钥和一个由证书授权机构颁发的证书。在本例中,我将使用自颁发的证书。
sudo yum install mod_ssl openssl
# 生成私钥
openssl genrsa -out smtp.key 2048
# 生成 CSR
openssl req -new -key smtp.key -out smtp.csr
# 生成自签名的钥匙
openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in smtp.csr -signkey smtp.key -out smtp.crt
# 将文件复制到正确的位置
cp smtp.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs
cp smtp.key /etc/pki/tls/private/smtp.key
cp smtp.csr /etc/pki/tls/private/smtp.csr
打开postfix配置文件,然后添加以下参数。
sudo vim /etc/postfix/main.cf
smtp_tls_security_level = may
smtpd_tls_security_level = may
smtp_tls_note_starttls_offer = yes
smtpd_tls_key_file = /etc/pki/tls/private/smtp.key
smtpd_tls_cert_file = /etc/pki/tls/certs
smtp_tls_CAfile = /etc/ssl/certs/ca.crt
smtp_tls_loglevel = 1
安全级别“may”意味着宣告对远程SMTP客户端上的STARTTLS的支持,但是客户端不需要使用加密。我在这里按照mailgun文档提示使用“may”,但是如果你想要强制使用TLS加密,可以使用“encrypt”。
service postfix restart
# 发送一封测试邮件
echo test mail | mail -s "test" test@yourdomain.com && sudo tail -f /var/log/maillog
你应该会看到以下信息
Aug 21 00:00:06 vps postfix/smtp[4997]: setting up TLS connection to smtp.mailgun.org[50.56.21.176]:587
Aug 21 00:00:06 vps postfix/smtp[4997]: Trusted TLS connection established to smtp.mailgun.org[50.56.21.176]:587: TLSv1.2 with cipher AES256-GCM-SHA384 (256/256 bits)
如果一切正常,你可以注释掉以下参数。
“smtp_tls_loglevel = 1”
二 : Linux服务器Cache占用过多内存导致系统内存不足问题的排查解决
作者:大圆那些事| 文章可以转载,请以超链接形式标明文章原始出处和作者信息
网址:
问题描述
Linux服务器内存使用量超过阈值,触发报警。(www.61k.com]
问题排查
首先,通过free命令观察系统的内存使用情况,显示如下:
total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 24675796 24587144 88652 0 357012 1612488 -/+ buffers/cache: 22617644 2058152 Swap: 2096472 108224 1988248
其中,可以看出内存总量为24675796KB,已使用22617644KB,只剩余2058152KB。
然后,接着通过top命令,shift + M按内存排序后,观察系统中使用内存最大的进程情况,发现只占用了18GB内存,其他进程均很小,可忽略。
因此,还有将近4GB内存(22617644KB-18GB,约4GB)用到什么地方了呢?
进一步,通过cat /proc/meminfo发现,其中有将近4GB(3688732 KB)的Slab内存:
...... Mapped: 25212 kB Slab: 3688732 kB PageTables: 43524 kB ......
Slab是用于存放内核数据结构缓存,再通过slabtop命令查看这部分内存的使用情况:
OBJS ACTIVE USE OBJ SIZE SLABS OBJ/SLAB CACHE SIZE NAME 13926348 13926348 100% 0.21K 773686 18 3494744K dentry_cache 334040 262056 78% 0.09K 8351 40 33404K buffer_head 151040 150537 99% 0.74K 30208 5 120832K ext3_inode_cache
发现其中大部分(大约3.5GB)都是用于了dentry_cache。
问题解决
1. 修改/proc/sys/vm/drop_caches,释放Slab占用的cache内存空间(参考drop_caches的官方文档):
Writing to this will cause the kernel to drop clean caches, dentries and inodes from memory, causing that memory to become free. To free pagecache: * echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches To free dentries and inodes: * echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches To free pagecache, dentries and inodes: * echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches As this is a non-destructive operation, and dirty objects are notfreeable, the user should run "sync" first in order to make sure allcached objects are freed. This tunable was added in 2.6.16.
2. 方法1需要用户具有root权限,如果不是root,但有sudo权限,可以通过sysctl命令进行设置:
$sync $sudo sysctl -w vm.drop_caches=3 $sudo sysctl -w vm.drop_caches=0 #recovery drop_caches
操作后可以通过sudo sysctl -a | grep drop_caches查看是否生效。
3. 修改/proc/sys/vm/vfs_cache_pressure,调整清理inode/dentry caches的优先级(默认为100),LinuxInsight中有相关的解释:
At the default value of vfs_cache_pressure = 100 the kernel will attempt to reclaim dentries and inodes at a “fair” rate with respect to pagecache and swapcache reclaim. Decreasing vfs_cache_pressure causes the kernel to prefer to retain dentry and inode caches. Increasing vfs_cache_pressure beyond 100 causes the kernel to prefer to reclaim dentries and inodes.
具体的设置方法,可以参考方法1或者方法2均可。
参考资料
https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/sysctl/vm.txt
http://major.io/2008/12/03/reducing-inode-and-dentry-caches-to-keep-oom-killer-at-bay/
http://linux-mm.org/Drop_Caches
扩展:cache服务器 / primocache服务器版 / cache服务器是什么
三 : 详解Linux系统下PXE服务器的部署过程
在大规模安装服务器时,需要批量自动化方法来安装服务器,来减少日常的工作量.
但是批量自动化安装服务器的基础是网络启动服务器(bootserver).
下面我们就介绍一下 网络启动服务器的 安装和配置方法,供大家实践之用!
1. 本文用到的术语解释
PXE
PXE(Pre-boot Execution Environment)是由Intel设计的协议,它可以使计算机通过网络而不是从本地硬盘、光驱等设备启动。现代的网卡,一般都内嵌支持PXE的ROM芯片。当计算机引导时,BIOS把PXE client调入内存执行,并显示出命令菜单,经用户选择后,PXE client将放置在远端的操作系统通过网络下载到本地运行.
DHCP
DHCP(Dynamic Host Control Protocol) 动态主机控制协议.用于集中、动态的给客户机分配IP地址.
TFTP
TFTP(trivial file transfer protocol),一种开销很小的文件传输协议,语法类似ftp.因简单、高效,常用于网络设备的OS和配置更新.
2. PXE 原理
2.1. PXE Client Api (架构)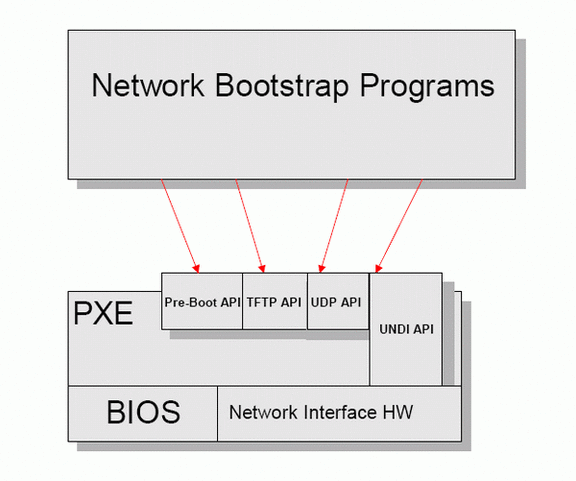
图 PXE API架构图。(图片来源:PXE Specification Version 2.1)
上图说明: 当BIOS把PXE Client载入记忆体,此时便具有DHCP Client及TFTP Client的能力。
PXE Client具备DHCP Client能力,可以透过DHCP Server来取得IP位址。
PXE Client具备TFTP Client能力”,可通过TFTP来下载kernel image等文件。
2.2. PXE启动流程图(pxe boot)
上图启动流程说明如下:
PXE Client 向 UDP 67端口 广播 DHCPDDISCOVER 消息.
DHCP SERVER 或者 DHCP Proxy 收到广播消息后,发送DHCPOFFER(包含ip地址)消息 到 PXE Client的 68 端口.
PXE Client 发送 DHCPREQUEST 消息到 DHCP SERVER ,获取启动文件(boot file name).
DHCP SERVER 发送DHCPACK(包含Network Bootstrap Program file name)消息 到PXE Client.
PXE Client 向 Boot Server 获取 NBP(Network Bootstrap Program) 文件.
PXE Client 从TFTP SERVER 下载 NBP,然后在客户端执行NBP文件
注意: 在NBP执行初始化后,NBP会按照自己默认的方式从TFTP SERVER中下载其他所需的配置文件.
这个时候 PXE 启动流程已经完成了,剩下的工作都是有NBP来执行完成的.
例如: pxelinux.0(NBP) 他会下载 default 配置文件,来显示菜单,根据需要启动不同的kernel image.
如果是RIS(window安装)的NBP,会启动 Windows boot loader 来执行安装部署widows任务.
3. PXE BOOT Server 配置过程
以下配置和测试 都是在 Centos5 上完成的,其他系统请酌情参考!
3.1. DHCP的安装与配置
在PXE引导过程中,PXE Client通过DHCP Server 获取ip地址,NBP文件名称,然后从TFTP SERVER 下载NBP文件并在客户端执行,从而启动计算机。
请确认系统中安装 dhcp 软件包
编辑 /etc/dhcpd.conf 配置文件,配置文件内容如下
[root@linux]# cat /etc/dhcpd.conf
ddns-update-style interim;
allow booting; #定义能够PXE启动
allow bootp; #定义支持bootp
next-server 192.168.0.1; #TFTP Server的IP地址
filename "pxelinux.0"; #bootstrap 文件(NBP)
default-lease-time 1800;
max-lease-time 7200;
ping-check true;
option domain-name-servers 192.168.0.1;
subnet 192.168.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0
{
range 192.168.0.128 192.168.0.220;
option routers 192.168.0.1;
option broadcast-address 192.168.0.255;
}
[root@linux]# /etc/init.d/dhcpd start
启动 dhcpd: [确定]
[root@linux]# chkconfig --level 35 dhcpd on
[root@linux]# cat /etc/xinetd.d/tftp
# default: off
# description: The tftp server serves files using the trivial file transfer
# protocol. The tftp protocol is often used to boot diskless
# workstations, download configuration files to network-aware printers,
# and to start the installation process for some operating systems.
# default: off
# description: The tftp server serves files using the trivial file transfer
# protocol. The tftp protocol is often used to boot diskless
# workstations, download configuration files to network-aware printers,
# and to start the installation process for some operating systems.
service tftp
{
socket_type = dgram
protocol = udp
wait = yes
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd
server_args = -s /tftpboot
disable = no
per_source = 11
cps = 100 2
flags = IPv4
}
[root@linux]# /etc/init.d/xinetd restart
[root@linux]# rpm -ql syslinux | grep "pxelinux.0"
/usr/lib/syslinux/pxelinux.0
[root@linux]# cp /usr/lib/syslinux/pxelinux.0 /tftpboot/
[root@linux]# mkdir /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg
[root@linux]# cat /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
default linux # 默认启动的是 'label linux' 中标记的启动内核
prompt 1 # 显示 'boot: ' 提示符
timeout 60 # 等待超时时间,单位为 1/10 秒,超时后自动启动 默认指定的label
display boot.msg # 显示boot.msg的内容,文件路径是相对tftp server 的根目录(默认 /tftpboot),所以boot.msg文件绝对路径在 /tftpboot/boot.msg .
F1 boot.msg # 按下'F1' 键后显示的文件
F2 options.msg
F3 general.msg
F4 param.msg
F5 rescue.msg
label 1 # 'label' 指定你在 'boot:' 提示符下输入的关键字。
kernel linux/rh44-x86-32/vmlinuz
append initrd=linux/rh44-x86-32/initrd.img ramdisk_size=8192 ks=http://install.test.com/conf/ks_module.cfg ksdevice=link
label 2
kernel linux/rh44-x86-64/vmlinuz
append initrd=linux/rh44-x86-64/initrd.img ramdisk_size=8192 ks=http://install.test.com/conf/ks_module.cfg ksdevice=link
label 3
kernel linux/rh46-x86-64/vmlinuz
append initrd=linux/rh46-x86-64/initrd.img ramdisk_size=8192 ks=http://install.test.com/conf/ks_module.cfg ksdevice=link
label 4
kernel linux/rh46-x86-32/vmlinuz
append initrd=linux/rh46-x86-32/initrd.img ramdisk_size=8192 ks=http://install.test.com/conf/ks_module.cfg ksdevice=link
label 5
kernel image/linux/rh38-x86-32/vmlinuz
append initrd=image/linux/rh38-x86-32/initrd.img ramdisk_size=8192 ks=http://install.test.com/conf/ks_module.cfg ksdevice=link
label 6
kernel linux/rh38-x86-64/vmlinuz
append initrd=linux/rh38-x86-64/initrd.img ramdisk_size=8192 ks=http://install.test.com/conf/ks_module.cfg ksdevice=link
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/01-88-99-aa-bb-cc-dd
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/C0A801C3
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/C0A801C
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/C0A801
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/C0A80
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/C0A8
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/C0A
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/C0
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/C
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
 本文标题:linux服务器系统-在Linux系统上使用转发服务器处理邮件通信的教程
本文标题:linux服务器系统-在Linux系统上使用转发服务器处理邮件通信的教程 61阅读| 精彩专题| 最新文章| 热门文章| 苏ICP备13036349号-1