一 : 循环队列操作
不是只有排序,二叉树才叫数据结构,面试栽在基本的数组和队列,链表,栈的有的是!!!本文对循环队列的重要操作作出总结。[www.61k.com]注:为了避免队列空和满两个状态混淆,
采用空闲一个位置的方式,即N个元素空间的循环队列最多只能存放N-1个有效元素。这也是大多数教材的做法。
1) 循环队列初始化:front=rear=0;
2)入队操作:rear=(rear+1)%size;
3)出队操作:front=(front+1)%size;
4)判断是否为空队列:front==rear;
5)判断队列是否已满:front=(rear+1)%size;
6)遍历队列各元素。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <malloc.h> #include <stdbool.h> //注意使用布尔类型时,需要引入此头文件 /******************************************************************************************************************* 定义循环队列的结构体。注:循环队列是在数组的基础上实现的,所以需要一个指向首元素的指针,另外头和尾用int来表示相对偏移量即可。 ********************************************************************************************************************/ typedef struct Queue { int * qBase; int front; int rear; }QUEUE; void initQueue(QUEUE *pq); void enQueue(QUEUE *pq , int value); bool isemptyQueue(QUEUE *pq); bool is_fullQueue(QUEUE *pq); void deQueue(QUEUE *pq , int *value); void traverseQueue( QUEUE *pq); /***************************************** 主函数测试入口 ********************************************/ int main(){ int val; QUEUE queue = {NULL,0,0} ; initQueue(&queue); enQueue(&queue,4); enQueue(&queue,5); enQueue(&queue,6); enQueue(&queue,7); enQueue(&queue,72); enQueue(&queue,42); traverseQueue(&queue); deQueue(&queue , &val); deQueue(&queue , &val); traverseQueue(&queue); enQueue(&queue,55); enQueue(&queue,65); traverseQueue(&queue); return 0; } /**************************************初始化一个空的循环队列 ******************************************/ void initQueue(QUEUE *pq){ pq->qBase = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*6); if(pq->qBase == NULL){ printf("内存分配失败!n"); exit(-1); } pq->front = pq->rear = 0; } /***************插入一个新元素 注:插入前需要先判断该队列是否已满,避免覆盖有效数据******************/ void enQueue(QUEUE *pq , int value){ if(is_fullQueue(pq)){ printf("循环队列已满,拒绝插入%d!n",value); } else{ pq->qBase[pq->rear] = value; pq->rear = (pq->rear + 1)%6 ; printf("n %d 入队 n" , value); } } /************** 删除一个元素,并通过指针返回该数 注:删除前要判断该队列是否为空。*******************/ void deQueue(QUEUE *pq , int *value){ if(isemptyQueue(pq)){ printf("循环队列已空!"); } else{ *value = pq->qBase[pq->front]; printf("n %d 出队 n",*value); pq->front = (pq->front + 1)%6 ; } } /************************************ 判断循环队列是否为空 ************************************/ bool isemptyQueue(QUEUE *pq){ if(pq->front == pq->rear){ return true; } else return false; } /************************************ 判断循环队列是否已满 ************************************/ bool is_fullQueue(QUEUE *pq){ if((pq->rear +1)%6 == pq->front){ return true; }else return false; } /************************************* 遍历循环队列中的各元素 *************************************/ void traverseQueue( QUEUE *pq){ if(isemptyQueue(pq)){ printf("循环队列为空!n"); exit(0); } printf("当前循环队列 :n"); printf("front是%d,rear是%d :n",pq->front,pq->rear); int tail = pq->front ; while(tail != pq->rear){ printf(" %d ",pq->qBase[tail]); tail = (tail + 1)%6; } }二 : 队列之顺序队列与循环队列
一、队列的概念 只能在表的一端进行插入操作,只能在表的另一端进行删除操作,这种数据结构称为队列。把允许插入的一端叫队尾(rear),允许删除的一端叫对头(front)。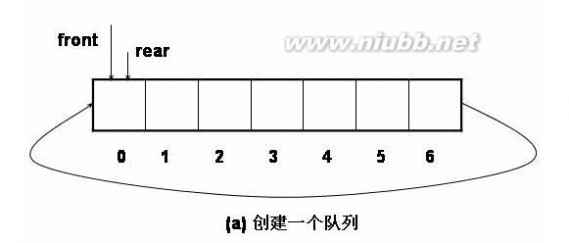
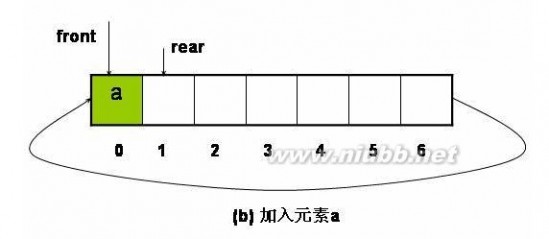
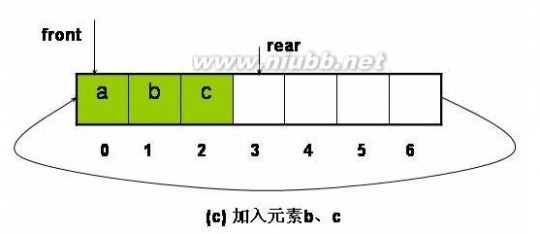
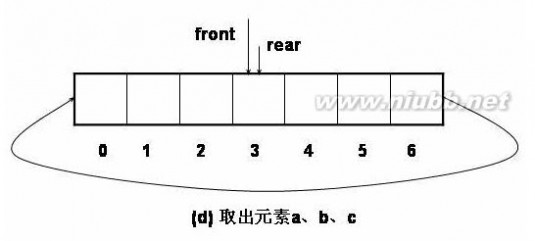
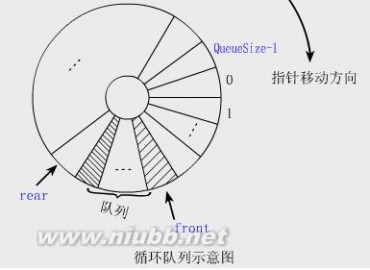 1、 循环队列的基本操作
1、 循环队列的基本操作
三 : 循环队列的基本操作
实验目的及要求:
了解和掌握循环队列的特点;
掌握循环队列基本操作的实现;
要求完成循环队列的初始化、入队、出队、求队列长度、显示操作的实现。 实验设备环境及要求:
PC机一台,内存要求128M以上,VC++6.0集成开发环境。
实验内容与步骤:
1、在VC++6.0环境中新建一个工程和C++文件;
2、实现循环队列初始化、入队、出队、求队列长度算法,代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MAXQSIZE 5
typedef char QElemType;
typedef struct {
QElemType *base;
int front;
int rear;
}SqQueue;
int InitQueue(SqQueue &Q){
Q.base = (QElemType *)malloc(MAXQSIZE*sizeof(QElemType));
if(!Q.base) return 0;
Q.front = Q.rear =0;
return 1;
}
int QueueLength(SqQueue Q){
return (Q.rear-Q.front+MAXQSIZE) % MAXQSIZE;
}
int EnQueue(SqQueue &Q,QElemType e){
if((Q.rear+1) % MAXQSIZE == Q.front) {
printf("队列为满队列!!n");
return 0;}
Q.base[Q.rear] = e;
Q.rear = (Q.rear+1) % MAXQSIZE;
return 1;
}
int DeQueue(SqQueue &Q,QElemType &e){ if(Q.front == Q.rear) return 0;
e = Q.base[Q.front];
Q.front = (Q.front+1) %MAXQSIZE; return 1;
}
void DispQueue(SqQueue Q){
int m,i;
m = QueueLength(Q);
if(m ==0) printf("该队列为空队列!!n"); for(i = Q.front; i%MAXQSIZE!=Q.rear; i++) printf("%c",Q.base[i]);
printf("n");
}
void main(){
SqQueue Q;
QElemType e;
InitQueue(Q);
DispQueue(Q);
EnQueue(Q,'A');
EnQueue(Q,'B');
EnQueue(Q,'C');
EnQueue(Q,'D');
printf("队列长度为:");
printf("%dn",QueueLength(Q));
printf("队列为:");
DispQueue(Q);
DeQueue(Q,e);
printf("队列长度为:");
printf("%dn",QueueLength(Q));
printf("队列为:");
DispQueue(Q);
EnQueue(Q,'E');
printf("队列长度为:");
printf("%dn",QueueLength(Q));
printf("队列为:");
DispQueue(Q);
EnQueue(Q,'F');
printf("队列为:");
DispQueue(Q);
}
实验指导与数据处理:
实验结果:该队列为空队列!!
队列长度为:4
队列为:ABCD
队列长度为:3
队列为: BCD
队列长度为:4
队列为: BCDE
队列为满队列!!
队列为: BCDE
分析讨论:
本次实验通过对循环队列基本操作的实现,加深了对循环队列特点的理解,并且熟悉了VC++6.0集成环境,虽然在调试过程中遇到一些问题,但经分析后达到了预期的结果。
四 : 循环队列的基本操作
实验目的及要求:
了解和掌握循环队列的特点;
掌握循环队列基本操作的实现;
要求完成循环队列的初始化、入队、出队、求队列长度、显示操作的实现。(www.61k.com) 实验设备环境及要求:
PC机一台,内存要求128M以上,VC++6.0集成开发环境。
实验内容与步骤:
1、在VC++6.0环境中新建一个工程和C++文件;
2、实现循环队列初始化、入队、出队、求队列长度算法,代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MAXQSIZE 5
typedef char QElemType;
typedef struct {
QElemType *base;
int front;
int rear;
}SqQueue;
int InitQueue(SqQueue &Q){
Q.base = (QElemType *)malloc(MAXQSIZE*sizeof(QElemType));
if(!Q.base) return 0;
Q.front = Q.rear =0;
return 1;
}
int QueueLength(SqQueue Q){
return (Q.rear-Q.front+MAXQSIZE) % MAXQSIZE;
}
int EnQueue(SqQueue &Q,QElemType e){
if((Q.rear+1) % MAXQSIZE == Q.front) {
printf("队列为满队列!!n");
return 0;}
Q.base[Q.rear] = e;
Q.rear = (Q.rear+1) % MAXQSIZE;
循环队列 循环队列的基本操作
return 1;
}
int DeQueue(SqQueue &Q,QElemType &e){ if(Q.front == Q.rear) return 0;
e = Q.base[Q.front];
Q.front = (Q.front+1) %MAXQSIZE; return 1;
}
void DispQueue(SqQueue Q){
int m,i;
m = QueueLength(Q);
if(m ==0) printf("该队列为空队列!!n"); for(i = Q.front; i%MAXQSIZE!=Q.rear; i++) printf("%c",Q.base[i]);
printf("n");
}
void main(){
SqQueue Q;
QElemType e;
InitQueue(Q);
DispQueue(Q);
EnQueue(Q,'A');
EnQueue(Q,'B');
EnQueue(Q,'C');
EnQueue(Q,'D');
printf("队列长度为:");
printf("%dn",QueueLength(Q));
printf("队列为:");
DispQueue(Q);
DeQueue(Q,e);
printf("队列长度为:");
printf("%dn",QueueLength(Q));
printf("队列为:");
DispQueue(Q);
EnQueue(Q,'E');
printf("队列长度为:");
printf("%dn",QueueLength(Q));
printf("队列为:");
DispQueue(Q);
EnQueue(Q,'F');
printf("队列为:");
循环队列 循环队列的基本操作
DispQueue(Q);
}
实验指导与数据处理:
实验结果:该队列为空队列!!
队列长度为:4
队列为:ABCD
队列长度为:3
队列为: BCD
队列长度为:4
队列为: BCDE
队列为满队列!!
队列为: BCDE
分析讨论:
本次实验通过对循环队列基本操作的实现,加深了对循环队列特点的理解,并且熟悉了VC++6.0集成环境,虽然在调试过程中遇到一些问题,但经分析后达到了预期的结果。(www.61k.com]
五 : C++类模板实现循环队列

以下是本人用C++类模板实现的一种数据结构——循环队列。希望对人们有所帮助,也希望人们提出宝贵的意见!
//循环队列
#ifndef _QUEUE_H_INCLUDED
#define _QUEUE_H_INCLUDED
template<typename T>
class _queue
{
public:
_queue(size_t _capacity = 1):capacity(_capacity), length(0), pBase(new T[_capacity]),
pHead(pBase), pLast(pBase){}
~_queue(){delete []pBase;}
void ClearQueue()
{
pHead = pBase;
pLast = pBase;
length = 0;
}
bool IsEmpty()const {return !length;}
size_t GetLength()const {return length;}
T& GetHead()const {return *pHead;}
void Push(T &e);
T Pop();
void vist();
private:
void NewMenory();
void Insert(T &e);
size_t capacity;
size_t length;
T *pBase;
T *pHead;
T *pLast;
};
template<typename T>
void _queue<T>::NewMenory()
{
T *ptmpNew(new T[2*capacity]);
T *ptmpNewCopy(ptmpNew);
T *ptmpheadCopy(pHead);
T *ptmplimit(pBase + capacity -1);
for(int i = 0; i <capacity; ++i)
{
*ptmpNewCopy = *ptmpheadCopy;
if(ptmpheadCopy == ptmplimit)
{
ptmpheadCopy = pBase;
continue;
}
++ptmpNewCopy;
++ptmpheadCopy;
}
delete []pBase;
pBase = ptmpNew;
pHead = pBase;
pLast = pBase + capacity;
capacity *= 2;
}
template<typename T>
void _queue<T>::Insert(T &e)
{
if(pLast != (pBase + capacity))
{
*pLast = e;
++pLast;
}
else
{
*pBase = e;
pLast = pBase + 1;
}
}
template<typename T>
void _queue<T>::Push(T &e)
{
++length;
if(length > capacity)
NewMenory();
Insert(e);
}
template<typename T>
T _queue<T>::Pop()
{
if(length > 0)
{
--length;
if(pHead == pBase + capacity -1)
{
T tmp(*pHead);
pHead = pBase;
return tmp;
}
return *(pHead++);
}
return *pBase;
}
template<typename T>
void _queue<T>::vist()
{
T *ptmphead(pHead);
T * const ptmplimit(pBase + capacity);
for(int i = 0; i<length; ++i)
{
if(ptmphead == ptmplimit)
ptmphead = pBase;
std::cout<<" '"<<*ptmphead<<"' ";
++ptmphead;
}
}
#endif // _QUEUE_H_INCLUDED
 本文标题:循环队列-循环队列操作
本文标题:循环队列-循环队列操作 61阅读| 精彩专题| 最新文章| 热门文章| 苏ICP备13036349号-1