一 : 柴油发电机工作原理的维修保养
柴油发电机工作原理 -维修保养A级保养
l)检查发电机工作日报;
2)检查发电机机油平面、冷却液平面;
3)日检发电机有无损坏、渗漏,皮带是否松弛或磨损;
4)检查空气滤清器,清洁空气滤清器芯子,必要时更换;
5)放出燃油箱及燃油滤清器中的水或沉积物;
6)检查水过滤清器;
7)检查起动蓄电池及电池液,必要时添加补充液;
8)起动发电机并检查有无异响;
9)用空气枪清洁水箱、冷却器及散热网灰尘。
(www.61k.com)B级保养
1)重复A级每日的检查;
2)每100至250小时,要更换柴油滤清器;
所有柴油滤清器不可清洗.只可更换。100至250小时只是一个弹性时间,必须要根据柴油实际的清洁程度而更换;
3)每200至250小时,要更换发电机机油及机油滤清器;
机油必须要符合美国APICF级以上;
4)更换空气滤清器(机组运行300-400小时);
要重视机房环境而决定更换空气滤清器的时间,此滤清器是可以用气枪清洁;
5)更换水过滤清器及添加DCA浓度;
6)清洗曲轴箱呼吸阀滤网。
C级保养
机组运行2000-3000小时,请进行如下工作:
重复A、B级保养
1)拆下气门室盖,清洗油污、油泥;
2)紧固各部螺丝(包括运行部分、固定部分);
3)用引擎洁霸清洗曲轴箱、油泥、铁屑及沉积物;
4)检查涡轮增压器的磨损程度并清洗积炭,必要时进行调校;
5)检查、调整气门间隙;
6)检查PT泵、喷油器工作情况,调整喷油器行程,必要时进行调校;
7)检查、调整风扇皮带、水泵皮带的松紧,必要时进行调整或更换:清洗水箱散热网,并检查节温器的使用性能。
小修
l)检查气门,气门座等磨损程度,必要时进行修理或更换;
2)检查PT泵,喷油器的工作状况,必要时进行修理、调校;
3)检查、调整连杆及各紧固螺丝的扭力矩;
4)检查、调整气门间隙;
5)调整喷油器行程;
6)检查调整风扇充电机皮带的张紧度;
7)清洗进气支管的积炭;
8)清洗中冷器芯;
9)清洗整个机油润滑系统;
10)清洗摇臂室、油底壳的油泥及金属铁屑。
中修
1)含小修项目;
2)分解发动机(除曲轴外);
3)检查缸套、活塞、活塞环、进排气门、等曲柄连杆机构、配气机构、润滑系统、冷却系统的易损零件,必要时更换;
4)检查燃料供给系统,调校油泵油咀;
5)发电机电球修理检测,清净油污沉积物,润滑电球轴承。
大修
1)含中修项目;
2)解体全部发动机;
3)更换气缸体、活塞、活塞环、大小轴瓦、曲轴止推垫、进排气门、全套发动机大修包;
4)调校油泵、喷油器、更换泵芯、喷油头;
5)更换增压器大修包、水泵修理包;
6)校正连杆、曲轴、机体等部件,必要时修复或更换。
保养方法
每天保养
1.检查柴油发电机工作日报。
2.检查柴油发电机:机油平面,冷却液平面。
3.日检柴油发电机有无损坏、掺漏,皮带是否松弛或磨损。
每周保养
1.重复每日的A级柴油发电机检查。
2.检查空气滤清器,清洁或更换空气滤清器芯子。
3.放出燃油箱及燃油滤清器中的水或沉积物。
4.检查水过滤器。
5.检查起动蓄电池。
6.起动柴油发电机并检查有无影响。
7.用空气枪及清水冼冷却器前后端的散热片。
维护保养
柴油发电机组仅限于以下维护手段:
对机组的四漏现象、表面、启动电池、机油和燃油等的检查;
清洁改善机房环境,定期更换三滤;
每月进行空载,每半年进行加载试机等方面维护;
使用电源监控进行实时观测电质量参数。
现有维护手段局限性:
现有维护中的加载测试也只是对后端现有用电设备的带载测试,存在一定风险,并且功率较低;
更换三滤或经过大修没有科学依据;
更换三滤或经过大修后,没有专门负载进行加载试机,不清楚是否能达到预期目的;
空载试机和小功率带载产生的大量积碳。
柴油发电机是一种独立的发电设备,主要是在停电时提供应急电源。事实上,机组绝大部分时间处于待机备用状态,实际投入使用的机会比较少,平时多以试机为主,缺乏较完善的检测、维修手段。但这种应急备用电源是不可缺少的。如何做到发电机在平时使用较少的情况下,应急时能及时供电,运行安全可靠,停电结束后又能立即停机。
第一,电池组的检查。由于备用电源不是经常投入使用,发电机是否能正常启动,关键在于电池的维护保养。如电池组出现了问题,比较常见的情况是:有电压无电流,这时可以听到启动电机内电磁阀吸合的声音,但带不动连轴。电池组出现问题导致无法停机原因有三:1.在试机时采用停止为电池充电的方式,会导致电池电量不足。2.采用机械油泵由皮带传动,额定转速下的泵油量很大,然而电池组供电不足,导致停机时截流阀里的弹簧片由于电磁阀吸力不够而不能封死从四个出油孔喷出的燃油,造成不能停机。3.国产电池通常寿命为两年,没有定期更换。
第二,启动电磁阀的检查。发电机在运行时,人们总结出“一看、二听、三摸、四嗅”的一套检查方法。启动时的听,是一个很重要的步骤。以美国原装康明斯发电机为例,只需按下启动按钮,三秒钟之后,即可启动。在这三秒钟之内可听到两个“咔嗒”声。一旦听不到第二声响,就要检查启动电磁阀是否正常工作,若电磁线圈烧断,发电机当然就不能启动。
第三,柴油、润滑油的检查。因为机组长期处于静态,机组本身各种材料会与机油、冷却水、柴油、空气等发生复杂的化学、物理变化,从而将机组“放”坏。为此应注意油的问题。为了消防安全,通常都把柴油油箱放在一个密闭的房间内,由于大气中水气因温度的变化而发生冷凝现象,结成水珠挂附在油箱内壁,流入柴油中,致使柴油含水量超标,这样的柴油进入柴油机高压油泵,会锈蚀精密耦合件———柱塞,严重损坏机组。发电机润滑油是有保存期的,长时间存放,润滑油的物理化学性能会发生变化,造成机组工作时润滑状态恶化,容易引起发电机机件损坏。
A级保养
柴油发电机使用时,检查并记录发电机每小时的工作状态。(每小时检查并记录发电机的输出电压、频率、机油压力、水温、充电、排烟)
开机之前一定要检查机油量及冷却水位。(开机之前让机组空转8分钟后,听发电机声音正常时投入负载)
停机时待机组冷却后要清洗机组表面。(发电机先卸负载,空转十分钟后停机,以让增压气和点球得到充分冷却)
B级保养
重复A级保养工作。
检查电池水液面(一半要高于锌片1cm)。
检查各皮带的张紧度。
根据柴油质量,每200-300小时更换柴油油格。
每250-300小时更换机油及机油格。
没500-800小时更换风格(使用期间可用风枪吹1-2次)。
每500小时更换水格并添加防锈水。
每500小时或3个月检查控制线路。
清洁水箱散热网。
C级保养
重复B级保养(每3000-4000小时专业人员维护)。
每3000-4000小时清洁气门间隙及喷油咀柱塞行程进行调整。
每4000-5000小时清洁电球轴承并注入润滑油。
每4000-5000小时拆下增压器清楚积碳,有必要时要更换增压器修理包(该项工作可以延长增压器使用寿命)。
测试机组的保护装置性能(如:高水温、低电压、超速等自动停机)。
每3000-4000小时拆下PT泵清洗芯。
没3000-40000小时拆下启动马达检查碳刷及接触铜片。
每3000-40000小时拆下电池充电器检查碳刷及轴承。
做好以上三种保养完全能够使您的发电机中修延期到8000-10000小时,大修延期到一万五至一万八千小时。
故障检查
原则和方法
柴油发电机组故障的原因通常是多方面因素造成的,不同故障表现出不同的现象,要排除故障,必须先查明故障的原因,在实践中通过看、听、摸、嗅等感觉,来发现柴油机异常的表现,从而发现问题、解决问题,消除故障。
判断柴油机故障的一般原则是:结合结构、联系原理、弄清现象、结合实际,从简到繁、由表及里、按系分段、查找原因。
在长期的生产实践中,人们摸索总结出“一看、二听、三摸、四嗅”的一套检查方法,通过仪表监测和人体器官的感受,去观察和判断柴油机的运行情况。
运转异常
柴油机长期运转后,发生了故障,通常会遇到下列几种现象。
(1)运转时声音异常柴油机运转时发出不正常的敲击声、放炮声、吹嘘声、排气声、周期性的磨擦声等。
(2)运转异常柴油机不易启动、工作时出现剧烈震动,拖不动负载,转速不稳定等。
(3)外观异常柴油机排气管冒白烟、黑烟、蓝烟,各系统出现漏油、漏水、漏气等。
(4)温度异常机油温度或冷却水温度过高,轴承过热等。
(5)气味异常柴油机运行时,发出臭味、焦味、烟味等气味。
柴油发电机组运行进,发现上述异常现象后,必须进行仔细的调查,根据故障现象,分析判断找出故障的部位和原因。有时一种故障可能有好几种异常现象,例如高压油泵磨损后,既可表现启动困难,也可表现输出功率不足,还可表现低速运转不稳定等现象。有时一种异常现象,可能有几种故障造成的。因此,柴油机运行时出现异常现象,必须认真查清产生异常现象的原因,这就要求我们善于作分析推理判断,透过现象抓实质,找出发生故障的原因和部位,将故障排除。
检查方法
(1)根据异常的声响来判别故障的部位用一把通心改锥或用一根半米长一端磨尖的细铁条,进行“听针判断”,一端贴耳,另一端触及各检查部位表面,可较清晰地监听到异常声响产生的部位,声响的大小和性质。不同部位发出声响往往是不同的。例如主轴承间隙过大发生冲击声是沉闷的,气门与活塞碰击声是清脆的,若飞轮键槽配合松动发出“唝!唝!”的撞击声等等,因此,根据不同声响,来判断故障的部位。
(2)用局部停止法来判断经故障分析后,若怀疑故障是由某一汽缸引起的,可停止该缸工作,观察故障现象是否消失,从而确定故障原因和部位。例如柴油机冒黑烟,分析为某缸喷油嘴喷孔堵塞,可对该缸停止供油,若黑烟消失,说明判断正确。
(3)用比较法来判断根据故障分析,怀疑故障可能是由于某一零、部件所造成的,可将该零件(或部件)更换一只新件,然后开机运行比较柴油机前后工作情况是否有变化,从而找出故障原因。
(4)用试探法来判断根据分析故障原因一时难以判断,可用改变局部范围内的技术状态,观察柴油机工作性能是否有影响,以此来判别故障的原因。例如柴油机发不出规定的功率,怀疑某缸压缩冲程压力不足,是汽缸与活塞间隙较大密封不严造成的,此时将缸盖打开向汽缸注入少量机油,以改善密封状况,然后重新装好缸盖,开机试验若压力增大,输出功率增加,说明分析是正确的。
柴油发电机组经长时间使用后,其故障现象很多,由于柴油机各种型号不同,国产的和进口的其结构和使用环境不同,故障原因也有所不同,因此,在处理问题时,对具体问题应根据不同情况作具体分伯。正确分析和判断柴油机故障的原因,是一项细致的工作,不应在未弄清故障原因之前就乱拆一通,这样不但不能消除故障,而且可能在重装拆开的零、部件时,达到不技术要求造成新的故障。
故障解决
在现代工业的连续生产中,柴油发电机由于受工作温度、压力、震动等因素的影响,不可避免的出现渗漏问题。通常解决渗漏的传统方法是打卡具或焊补等工艺,但具有较大的局限性,且有的渗漏受工作环境安全的要求限制,无法现场进行解决。目前针对柴油发电机渗漏最新解决方案是采用高分子复合材料的方法,其中应用最为成熟的是美嘉华技术体系。用高分子材料修复柴油发电机是现场堵漏一个理想方法,特别是在易燃易爆场合下及不停车带压堵漏方面均显示其独有的优越性。不仅可以停车堵漏、密封,而且可以在不影响生产进行的前提下在线待机治理渗漏部位,达到重新密封的目的,经济效益显著。
高分子材料治理柴油发电机渗漏
发电机组电机受潮以后,必须及时进行烘干处理,根据电机的容量大小和受潮程度,常用的烘干方法有以下两种:
在有条件的地方,将电机整体(最好把定子和转于拆开)放到烘箱(炉)中逐渐升温烘烤.烘箱(炉)应能通风.以便带走电机内的潮气,并且最好是夹层的,里层放电机,在外层加热.里层的温度保持在90一100°C,而且不能有明火、烟尘以及其他可燃性和腐蚀性气体存在。一般要求连续烘烤8~18h,中间可测量几次电机的绝缘电阻值,直至达到规定值并且稳定为止。
交流后,在出线盒内将三相短接,然后使发电机转速上升到暂定转速,保持不变,再调节励磁电流,先使定子短路电流达到额定电流的50%~70%,保持4~5h,然后再增加励磁电流,使短路电流达到额定值的80%一100%,使线圈温度保持在85℃以下,每隔30min测量一次线圈的绝缘电阻和温度,直到绝缘电阻达到规定值井稳定为止。
发电机在进行就地干燥时,一定要做好必要的保温和现场安全措施,具体措施如下:
干燥时,发电机各处的温度限额为:
另外,在干燥过程中、要定时记录绝缘电阻、绕组温度、排出空气温度、铁芯温度的数值,并绘制出定子温度和绝缘电阻的变化曲线,受潮绕组在干燥初期,由于潮气蒸发的影响,绝缘电阻明显下降,随着干燥时间的增加,绝缘电阻便逐渐升高,最后在一定温度下,稳定在一定数值不变。若温度不变,且再经3~5小时后绝缘电阻及吸收比也不变。用摇表测量转子的绝缘电阻大于1MΩ时,则可认为干燥工作结束。
防止爆缸
冬天气温低,柴油发电机汽缸盖易爆缸。
主要缘由
1、起动后才加冷却水。柴油机起动后,柴油发电机内温度当即升高,假若这时参加冷却水,汽缸体与汽缸盖急剧冷却,就会因冷缩而裂缝。
2、停机后,没有放冷却水。机内水冻结成冰,体积增大,发作汽缸体和汽缸盖胀裂。
3、发电机组作业时,冷却水短少或水箱开锅机温过高,俄然参加冷却水。汽缸体和汽缸盖过冷缩短也会导致开裂。
4、发电机组长时辰作业,机内温度高,泊车后当即放掉高温水。会导致高温零件骤遇冷空气而开裂。
5、运用减压机停机,使高温的气缸盖俄然遇到酷寒空气而导致开裂。
汽缸开裂
1、起动柴油机前,应先给水箱参加温热水,严冬天节要灌注热水2~3次,待放水阀中流出的水约30~50℃时起动为佳。
2、柴油机作业时辰较长时,停机后应等候半个小时左右,机温下降到40~50℃时再放冷却水。放完水后最好用细铁丝捅通放水阀开关,避免沉淀物阻塞放水阀。
3、康明斯柴油发电机作业过热严厉缺水时,应让柴油机低速空转10~15分钟,然后再逐步参加冷却水
发电故障
可能原因
(1)停机后经常失去剩磁,是由于励磁机磁极所用的材料接近软钢,剩磁较小,停机后励磁绕组中没有电流时磁场就消失。
(2)发电机的磁极失去磁性。
(3)励磁回路元件损坏或线路有断路,短路或接地现象。
(4)励磁机电刷与换向器接触不良或刷架压力不足。
(5)励磁绕组接线错误,极性相反。
(6)发电机电刷与滑环接触不良,或电刷压力不足。
(7)发电机定子绕组或转子绕组断路。
(8)发电机引出线接线松动或开关接触不良。
(9)熔断器熔断
处理方法
(1)常备蓄电池,在发电前先进行充磁。
(2)在绕组中通入比额定电流大的直流电(时间很短)进行充磁,具体电流由试验决定。
(3)更换损坏元件,修复故障线路。
(4)清除接触表面的尖垢,调整电刷压力,紧固刷架。
(5)更正接线,按下确的极性充磁。
(6)清除接触表面尖垢,研磨电刷,调整理电刷压力,使电刷与滑环紧密接触。
(7)检查并修复断路处。
(8)连接好接头或修理开关接触部位。
(9)查明熔断原因,断定发电机本身及线路正常后,更换规定的熔断器。
进出口情况
这些年来,随着经济的不断发展,国产发电机行业也经历了翻天覆地的变化,发电机行业在我国已经变得越来越成熟,不仅能满足国内发电机的需求,而且已经进行了大量的出口,产品远销世界各地。今天,随着世界经济不景气的出现,国产发电机行业改如何面对,我们就换个大家一起来讨论一下。
长期以来作为柴油发电机组进口大国的中国,在2007年首次出现柴油发电机组出口数量、金额双双超出进口的局面。2007年、2008年出口金额同比增幅分别超过110%和50%。2009年在全球金融危机蔓延造成国际需求萎缩的背景下,中国柴油发电机组的出口出现了下滑,但出口金额仍远高于进口,依然呈现出较强的国际竞争力。随着全球经济复苏,以及新兴经济体及其他发展中国家对基础设施、工业建设、资源开发、交通运输等的强劲需求,我国柴油发电机组产品出口规模有望进一步扩大。
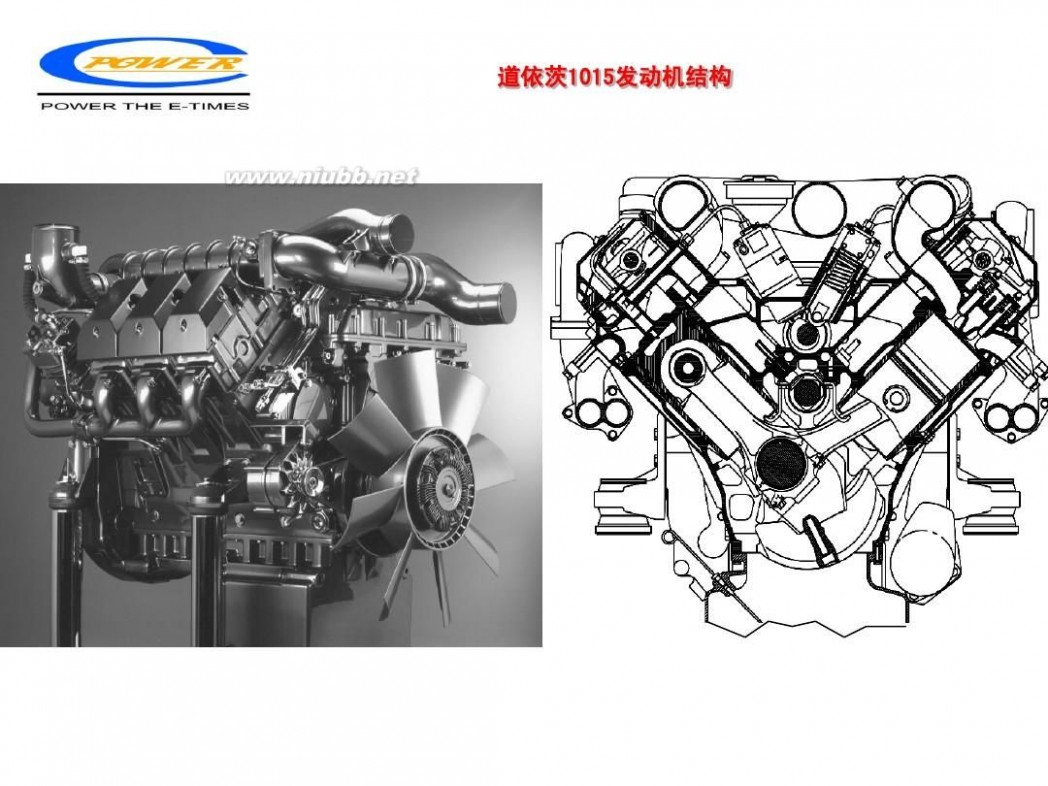
二 : 电喷柴油机发动机工作原理和系统技术介绍48
电喷柴油机发动机工作原理和系统技术介绍
船用柴油机是怎样工作的?
柴油机是一种内燃机,通过把燃油喷入高温高压的燃烧室而发火。船用柴油机是一种在船上使用的柴油机。其工作原理如下: 一定量的新鲜空气被吸入或泵入汽缸并被运动的活塞压缩至很高的压力。空气被压缩时,温度升高,便点燃喷入汽缸的油雾。燃油的燃烧增加了缸内空气的热量,使空气膨胀并迫使发动机活塞对曲轴做功,随之驱动螺旋桨。两次喷油期间的运转过程叫一个工作循环。它由一些程序固定的过程组成。这个循环可在两个行程或四个行程内完成。四冲程柴油机的工作循环需四个独立的活塞行程,即吸气,压缩,膨胀和排气。如果我们把吸气和排气行程与压缩和膨胀行程结合起来,四冲程柴油机就变成了二冲程柴油机。二冲程循环从活塞离开其行程底部,即下止点(BDC)向上运行开始,气缸侧面的进气口即扫气口是打开的,排气口也是打开的。经压缩的新鲜空气充入气缸,通过排气口将上一行程的残气吹出。 当活塞上行至其行程的1/5时,关闭进,排气口,随后空气在活塞上行中被压缩。当活塞上行到行程底部,即上止点(TDC)时空气的压力和温度都上升到很高的数值。此时喷油器把很细的油雾喷入灼热的空气中,燃烧开始,在气体中产生更高的压力。 随着高压气体的膨胀,活塞被推动下行直到它打开排气口,燃烧过的气体开始排出,活塞继续下行直到它打开进气口,另一个循环开始。
在二冲程柴油机中,曲轴转一星期产生一个动力行程,即做功行程;而在四冲程柴油机中,曲轴转两周才产生一个动力行程。这就是为什么从理论上说二冲程柴油机能产生相同尺寸的四冲程柴油机的两倍功率。然而,扫气不充分和其他损失使这一优势降到大约1.8倍。 在船上,每种柴油机都有他的应用。低速(即90~120 r/min)主推进柴油机以二冲程工作。在此低速时,机桨间不需减速箱。四冲程柴油机(通常以中速运转,转速在250~750r/min)用于发电机,并且有时作推进主机,用减速箱提供90~120 r/min的速度。
工作循环 柴油机可设计成以二冲程循环或四冲程循环工作,二者解释如下:
四冲程循环 典型的两转四冲程循环的过程。通常从上止点(TDC,发火)开始绘制,从上止点 (TDC,扫气)开始解释。上止点又叫内止点。
沿该顺时针看,开始时进,排气阀都是打开的(所有现代四冲程柴油机均有气阀机构)。如果柴油机是自然换气或带有径流增压气的小型高速机,气阀的重叠时间,即两气阀同时开启的时间将很短。排气阀将在上止点后(ATDC)10o左右关闭。
推进柴油机和绝大多数1000r/min以下运转的辅助发电柴油机几乎都采用涡轮增压,并设计成在这一时刻让大量的扫气空气贯穿流动以控制适当的叶片温度。在这种情况下,排气阀将保持开启直至上止点后50~60o关闭。随着活塞在其吸气行程向外或下止点下行,它将吸入大量新鲜空气。为使吸入空气量达到最大,并补偿因阀落座造成的开启量减少或吸气惯性作用,进气阀保持开启,直到下止点后大约25~30o(145~155oBTDC)。这一过程称之为进气阀关闭。充入的空气然后被上行的活塞压缩至大约550oC。依柴油机的型号和转速而定,大约在10o~20oBTDC,喷油器喷入精细雾化的燃油。喷入的燃油在2~7o内着火(也依机型而定),活塞在膨胀行程下行,在30~50o的期间内燃烧。活塞的运动通常有利于诱导空气助燃。
在大约120~150oATDC,排气阀打开(EVO)。这样选择正时能迅速将缸内气体排至排气管。这样可以:(a)保留足够的能量驱动废气涡轮增压器;(b)减小缸内压力在下止点时达最小值以减小排气行程消耗的泵气功。上行的活塞驱赶残留的废气,在70~80oBTDC,进气阀打开,这样向外流动的气体惯性加上正的压差(此时通常在汽缸中是存在的),就产生了空气对废气的贯穿气流以清扫汽缸。
如果柴油机是自然换气的,进气阀开启约在上止点前10o。工作循环重新开始。
二冲程循环
典型二冲程循环的过程,正如其名称所指,工作循环是在曲轴转一星期内完成的。
二冲程柴油机总是有进气口的,该气口被下行的活塞打开时使空气进入汽缸。废气可以经与邻近的排气口由同一活塞控制排出(回流扫气),或经气缸另一侧的排气口排出,或经排气阀排出(直流扫气)。
从上止点开始,燃烧已经进行。排气在上止点后110~120o开始,进气在随后20~30o,即上止点后130~150o开始迅速吹扫气缸。用这种方式,以音速流动的废气靠惯性促使空气迅速流过气缸,以产生最小的(新废气)掺混,因为所有未排出的废气都将降低用于下一行程的空气量。
在压缩行程,排气口应当在进气口前关闭以使充气量最大,但如果两个过程是同一活塞控制的,发动机的几何形状回妨碍实现这一点。这种情况可在有排气阀的柴油机中实现。
在任何情况下,进气口都将在下止点后,以和下止点前开启时相同的角度关闭,即在下止点后130~150o关闭,排气口在同样的角度范围内关闭。
喷油在上止点前约10~20o开始,角度依转速而定。燃烧同四冲程机一样持续30~50o
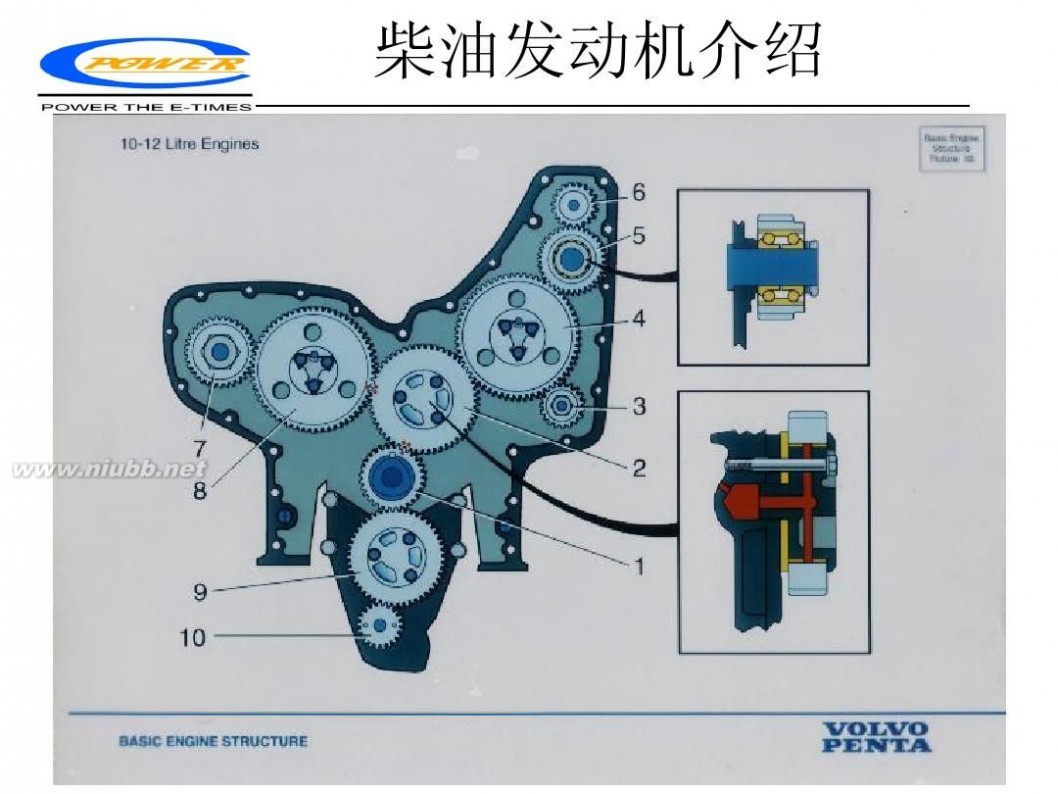
柴油机结构(I)
一、 机座和机架
机座在大多数情况下是焊接结构,用螺栓固定在构成船舶双层底的底座上。它在横向借助于侧楔垫螺栓,在纵向借助于端楔垫螺栓固定。
曲轴安放在机座横梁的轴承上,这些轴承称作主轴承。每个轴承由两块轴瓦组成,两块轴瓦由在机座上加工出的瓦座支撑,用双头螺栓和轴承盖固定。推力轴承位于发动机的尾部,可同机座制成一体也可同机座分开。
在机座上平面装有由若钢铸铁或锻钢制成的A字形机架,机架安装在机座的横梁上,并用螺栓固定。A形机架顶部有一个结实的框架结构叫扫气箱。该扫气箱分若干段,每段均带有垂直法兰,通过螺栓可将他们在链传动装置前1~3缸的部分连成一体,链传动装置后4~6缸的部分连成一体。链传动装置将曲轴和凸轮轴连在一起,封闭在链传动箱的壳体内。
二、 气缸和气缸盖
在扫气箱上部,每个气缸装有一个坚固的铸铁框架。这些框架称作气缸体或冷却水套,并带有垂直法兰,与扫气箱一样,可用螺栓将各框架连成首尾两组。
基座、机架和气缸用长贯穿螺栓连到一起,形成一个较大的坚实结构,减少了使用时产生的变形及振动。
气缸套有铸铁制成,缸套表面有时镀铬。气缸套向下延伸到扫气箱。缸套与扫气箱顶部的密封由橡胶圈实现,橡胶圈安装在缸套上切削的环槽内。在气缸套伸入扫气箱内的部位有一列称为扫气口的开口。气口的高度是这样布置的,当活塞位于下止点时,活塞上沿刚好打开气口。气口在缸套上以大约20o的倾角制成,其结果是使扫气旋转。
各缸顶部由特殊耐热钢制成的缸盖封闭。缸盖装在缸套顶部的平面上,并由机加工的凸肩定位。密封圈嵌入在缸盖锥形面时必须十分小心。气缸盖和气缸套用旋入缸体中的双头螺栓固定。
缸套上有钻空用于润滑,新型的缸套在其最上部还有钻空用于冷却。
每个缸盖上有一个大型中心孔,用于安装排气阀,还有两到三个空用于装喷油器,还有些孔用来安装起动阀、安全阀、示功阀、以及作为排气阀冷却水腔的进出口。
阅读材料译文
A.SULZER船用柴油机
SULZER RND-M 型柴油机是单作用、低速、二冲程、可逆转发动机。
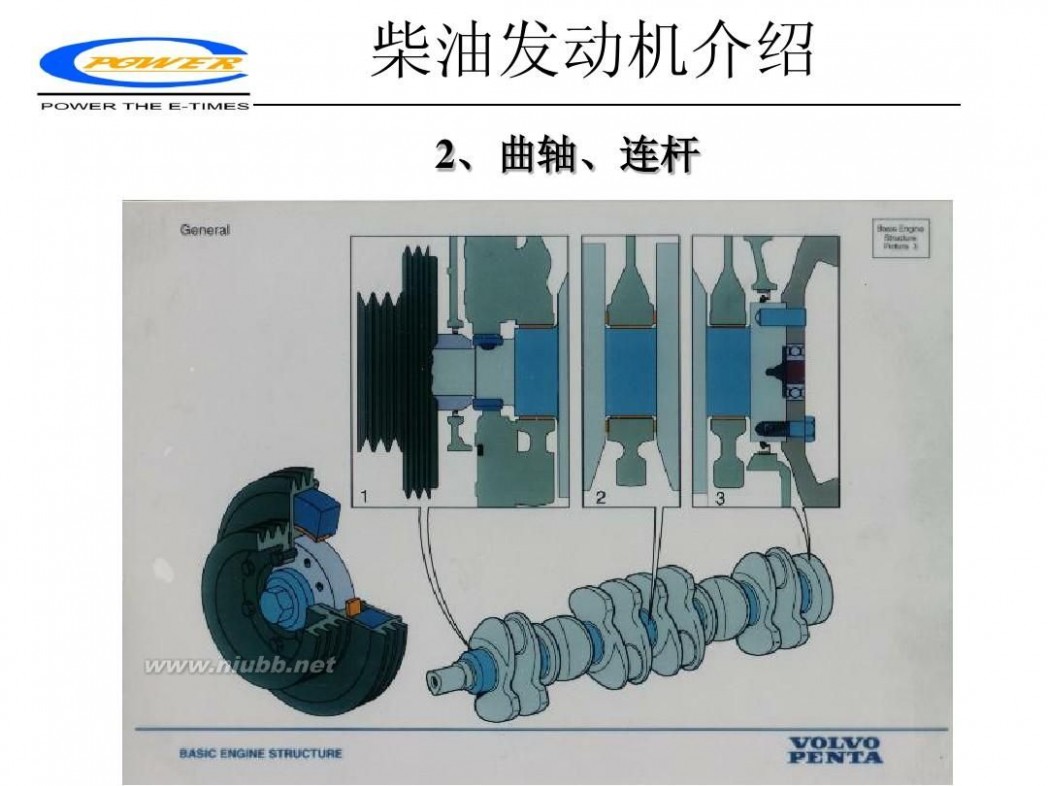
每个汽缸的运动机构由活塞、活塞杠、连杆及所连接的单柄曲轴组成。
机座制成纵向箱形梁的双壁结构。A形框架安装在机座上,支撑机架和气缸体,整个机座、A形框架和气缸体组件用贯穿螺栓连在一起形成一个刚性结构。为了承受曲轴横向弯曲负荷,主轴承盖由撑杆螺栓固定。这种强化结构对于承受经缸头传到柴油机结构上的燃烧负荷是必要的。曲轴是半组合式的,曲柄臂设计成部分平衡回转质量。气缸盖被制成单体件,并装有在中央的喷油器,起动空气阀、安全阀和示功阀。
废气驱动定压式的涡轮增压器提供扫气空气。采用回流式扫气并带有一台电动的自动运行的辅助鼓风机,以便低速和机动操作时使用。
润滑油供到低压和中压系统,低压系统向主轴承和其它轴承供油,十字头轴承由中压系统供油,铰链管把滑油送到十字头轴承。
汽缸、汽缸盖以及活塞由水冷却,伸缩套管把水送入活塞。
燃油喷射采用独立喷射系统,并且用Woodward型液压调速器调速。
RL型柴油机以RND-M型为基础,活塞行程加长,提供更大的输出功率和更低的转速。其新特征包括带有推力轴承的单壁机座、活塞头和其他主要燃烧室部件钻空冷却,及用水在接近热表面的钻空中循环。
BSULZER RTA 型柴油机
SULZER RTA84C是一种典型的低速二冲程十字头式长行程现代柴油机。其缸径为840mm,行程为2400mm,转速为100r/min,4 到12缸间均产品,也可特别为大型快速集装箱船生产。其设计及结构和RTA2型系列相似,RTA2系列使汽缸尺寸降到380mm。机座是由钢板和一些铸件焊接构成的单壁深墙箱形结构,在焊接的坚实A形机架上装有各冷却缸套,它们由螺栓连成一体形成缸体。这些机件组成了柴油机的强固整体框架。整个框架结构由贯穿螺栓垂直预紧。
缸套为铸铁合金。其上端是一坚实环台,坐落在汽缸体上,它承受很大的气体负载。缸套钻空冷却,可调节水流以维持合适的温度。缸套下端在扫气箱内,不进行冷却。在不同高度位置对气缸进行润滑以降低汽缸磨损率。
缸盖为坚实的锻钢件,采用钻孔冷却以减少热应力,并传递喷油器套的热量,使排气阀座用缸盖冷却水集中冷却。排气阀用84#镍铬钛合金(Ninonic80)制成,并通过安装在阀杆上的叶片转动。他靠液压开启,靠空气弹簧作用关闭,开启的液体压力来自凸轮驱动的操纵机构。
活塞带有合金钢的活塞头,并有5道压缩环,安装在镀铬的环槽内,活塞有一短的铸铁活塞裙。活塞用油冷却,既采用震荡冷却的方法,也采用小型喷嘴注射的方法,将油通入紧贴活塞头底面和在活塞环槽背面的孔中。冷却油通过活塞杆中的钻孔从十字头的铰接杆供入和返回。活塞杆与单体十字头上表面相连,并连续贯穿整个下半部和上端轴承。上端轴承材料为白合金,靠压力油润滑。十字头导向滑块与十字头各端相连。
半总成式曲轴采用倒角内缩的曲柄以增大主轴承面积,主轴承盖由装在机架内的撑杆螺栓固定。凸轮轴由齿轮驱动,配有伺服器以便在倒车运行时给燃油泵和起动空气分配器重新定时。
高压油泵为凸轮驱动阀式油泵,带可变发火定时调节,以保持低速时高效燃烧。每个高压油泵向对称布置的装在缸盖上不进行冷却的三个喷油器供油。在不喷油时热的燃油在喷油器中循环。
这种柴油机采用直流扫气,定压增压,带有高效的非冷却的透平增压器,在低速运行时,用两台高速电动辅助风机作补充。
柴油机结构(II)
一、 活塞及活塞杆
活塞由其下部一铸铁制成的活塞裙以及上部一耐热钢制成的活塞头组成。它们用螺栓连在一起并固定在活塞杆上。活塞部件相互间的位置由活塞头上车削的凹槽和定位销来固定。
每个活塞上装有5~6道活塞环,活塞环装在头部镀铬的环槽中。最上面的2~3道活塞环是带斜切口的窄环;紧接下去的2道活塞环是带有重叠搭口的宽环,最下面的那道环是刮油环。所有活塞环顶部和底部的外缘都稍有倒角,以便在新活塞环磨合期间缸套上留有油膜。
为了控制热应力,某些现代柴油机采用薄壁集中冷却活塞。在这种情况下,活塞头内部有一插件,它用来对冷却液流导向,以增强传统的“鸡尾震荡”效应。
活塞杆从顶部法兰到与十字头中心相对位置处镗孔。一根长管从此孔插入几近孔底。管的外径小于孔的直径,因此在活塞杆和管子之间形成一个环形空间。
活塞杆的下端直径减小,插入十字头内孔中,并用螺帽将十字头与活塞杆紧固。活塞杆上装有定位销,以确保各部件的正确装配。
在十字头两端轴颈处,各装有十字头滑块。十字头滑块由发动机机架内的十字头导板导向。十字头滑块在十字头上的位置由定位销确定,并用锥头螺栓紧固在十字头上。
EFI diesel engine works and system technology
Marine diesel engines is how does it work?
The diesel engine is an internal combustion engine, fuel is sprayed into the high temperature and pressure of the combustion chamber ignition. The marine diesel engine is a board used in diesel engines. Its working principle is as follows: a certain amount of fresh air to be sucked or pumped into the cylinder and piston compression to high pressure. When the air is compressed, the temperature, he ignited the oil mist sprayed into the cylinder. The increase in the heat of the cylinder air for fuel combustion, the air expansion and forcing the engine piston acting on the crankshaft, with the attendant drives a propeller. Twice the fuel injection during the operation process is called a cycle of work. It consists of some of the procedures process. This cycle can be completed within a two stroke or four stroke. The four-stroke diesel engine duty cycle required four separate piston stroke, that is, suction, compression, expansion and exhaust. If we inhale and exhaust stroke and the compression and expansion stroke combined, four-stroke diesel engine into a two-stroke diesel engines. Leave their itinerary at the bottom of two-stroke cycle piston bottom dead center (BDC) upward run began, the inlet of the cylinder on the side of the scavenging port is open, the exhaust port is open. Compressed fresh air charge into the cylinder, blowing out the residual gas on a trip through the exhaust port. When the piston up to 1/5 of his trip, close the intake, exhaust port, and then the air is compressed in the piston upward. When the piston up to trip the bottom of the top dead center (TDC), the air pressure and temperature rose to a high value. The injector to a very fine mist sprayed into the hot air, combustion gas to produce a higher pressure. With the expansion of the high-pressure gas, the piston is being pushed
downstream until it opens the exhaust port, combustion gas discharge, the piston continues downstream until it opens the air inlet, and another cycle begins.
Two-stroke diesel engine crankshaft revolution to produce a power stroke, power stroke; in the four-stroke diesel engine crank two weeks to produce a power stroke. This is why two-stroke diesel engine can produce twice the power of the same size four-stroke diesel engine theory. Scavenging, however, is not sufficient and other losses, this advantage dropped to about 1.8 times. On board, each diesel engine to have his application. Low-speed (90 ~ 120 r / min), main propulsion diesel two-stroke. This low speed, the machine paddle do not need gear boxes. Four-stroke diesel engine (usually in the medium-speed operation, the speed in the 250 ~ 750r/min) for generators, and sometimes for propulsion engines, gear box 90 ~ 120 r / min speed.
The duty cycle diesel engine can be designed as a two-stroke cycle or four-stroke cycle, the two are explained as follows:
Typical four-stroke cycle to turn the course of four-stroke cycle. Usually from the top dead center (TDC, ignition) to start drawing from the top dead center (TDC, sweep gas) begin to explain. The point is also called TDC TDC.
See along the clockwise, starting forward, the exhaust valves are open (all modern four-stroke diesel engines have valve bodies). If the diesel engine is a natural ventilation or a small high-speed machine with a the runoff pressurized gas, the valve overlap time, the two valves open at the same time a very short time. Close the exhaust valve at TDC (the ATDC) about 10 o.
Propulsion diesel engines and auxiliary power diesel engine operation following the vast majority of 1000r/min almost all turbocharged, and are designed so that at this moment a lot of scavenging air throughout the flow in order to control the leaf temperature. In this case, the exhaust valve will remain open until the shut down of 50 ~ 60 ° after top dead center. With the piston in its inspiratory stroke out or the next stop point downstream, it will inhale a large quantity of fresh air. Reaches the maximum, and compensation for the amount of air inhaled valve seated open reduction or the suction effect of inertia, the intake valve remains open, until the ending point of about 25 ~ 30 o (145 ~ 155 o BTDC). This process is called the intake valve closed. Filled the air and then upward piston compression to about 550 o C. Depending on the type and speed of the diesel engine, about 10 o ~ 20 o BTDC, the fuel injector is injected into a finely atomized fuel. Ignition of fuel sprayed into the 2 ~ 7 o (also according to the model), downstream of the piston in the expansion stroke, combustion period of 30 to 50 o. The piston movement is usually conducive to the induction of air for combustion.
Approximately 120 to 150 o the ATDC, the exhaust valve opens (EVO). Select is quickly cylinder gas emissions to the exhaust pipe. This: (a) to retain enough energy to drive exhaust gas turbocharger; (b) reduce the cylinder pressure to the next stop point of the minimum to reduce the consumption of the pump exhaust stroke Qigong. Residual exhaust gas upstream of the piston driven, 70 ~ 80 o BTDC, the intake valve open, so that outward flow of gas inertia coupled with a positive pressure differential (often in the cylinder in there), the air on the exhaust throughout the airflow to clean up the cylinder.
If the diesel engine is natural ventilation, the intake valve opens at about 10 o before TDC. Duty cycle to start again. Two-stroke cycle
Typical two-stroke cycle process, as its name within the meaning of the work cycle is completed within the crankshaft revolution.
Two-stroke diesel engine is always a piston to open the inlet, the air intake downstream air entering the cylinder. The exhaust gas can be discharged and the adjacent exhaust ports controlled by the same piston (return sweep gas), or through the exhaust port of the cylinder on the other side of the discharge, or discharge (DC sweep gas through the exhaust valve).
From TDC, the combustion has been carried out. 110 to 120 o after top dead center, exhaust intake in the next 20 to 30 o, the only point of 130 ~ 150 o quickly purge the cylinder. By inertia to promote in this way to the sonic flow of exhaust air rapidly flows through the cylinder to a minimum of (gas) mixing, because all is not the exhaust air will reduce the amount of air for the next trip.
In the compression stroke, the exhaust port should be closed before the inlet to the aeration rate, but if the two
processes is controlled by the same piston, and the geometry of the engine back to hinder the achievement of this. This situation in diesel engine exhaust valve.
In any case, the air intake will be the next stop point to open before the bottom dead point of view off, the next stop point 130 ~ 150 o turn off the exhaust port is closed in the same angle in the range.
The fuel injection before top dead center, about 10 ~ 20 o angle according to speed. Burning with the four-stroke machine is the same for 30 ~ 50 o
Diesel engine structure (I)
, Frame and rack
Base in most cases welded structure, bolted to the base constitute the double bottom of the ship. In the horizontal by means of lateral wedge pad bolt in the vertical by means of the end of the wedge pad bolt.
The crankshaft is placed in the base beam bearings, these bearings are referred to as the main bearings. Each bearing consists of two bearing two bearing from the bearing seat of the processing on the base support, a fixed stud and bearing cap. The thrust bearing is located in the rear of the engine, with the base made of one with the base unit separately.
A shape made of cast iron or steel of if steel rack on the base plane is equipped with rack-mount on the base beam and bolted. A shaped top of the rack has a sturdy frame structure called scavenge. The sweep gas tank divided into several sections, each with a vertical flange in front of the chain drive device through bolt a 3 cylinder parts fused to a chain drive device 4 to 6 cylinder part of the fused . The chain gear to the crankshaft and camshaft together, enclosed within the shell of the chain drive box.
Second, the cylinder and cylinder head
The upper part of the scavenge each cylinder is equipped with a sturdy cast iron frame. Framework known as the cylinder block cooling water jacket, and with a vertical flange, and scavenge available bolts to each frame into both the two groups.
Pedestal, rack and cylinder connected to a long through bolts together to form a solid structure, reducing the use of deformation and vibration.
Cylinder liner made of cast iron cylinder liner surface is sometimes chrome plated. Cylinder liner extending down to scavenge. Liner and scavenging box at the top of the seal by the rubber ring, rubber ring is installed in the liner on the cutting of the ring slot. One called scavenging port openings in the cylinder liner inserted into the sweep gas tank parts. The air inlet height is such arrangement, when the piston at bottom dead center, piston along just to open the air intake. The air inlet in the cylinder liner is made of about 20 o angle, the result is the scavenging rotation.
The top of each cylinder made of special heat-resisting steel cylinder head closed. Cylinder head mounted on the liner at the top of the plane, the orientation of the shroud by machining. Ring embedded in the cylinder heads of cone surface must be very careful. Cylinder head and cylinder to apply spin into the stud in the cylinder is fixed. Liner on the drilling space is used for lubrication, the new liner at the top of air drilling for cooling.
Each cylinder head has a large center hole used to install the exhaust valve, as well as two to three empty for loading injector, and also some of the holes used to install the starter valve, safety valves, indicator valve, as well as The exhaust valve cooling water chamber of import and export.
Reading material translation
A. SULZER marine diesel engine
Of SULZER the RND-M type diesel engine is single acting, low-speed, two stroke reversible engine.
The movement of bodies of each cylinder by the piston, the piston bar, rod and connected to a single handle crank. The docking station made of double-wall structure of the longitudinal box girder. A-shaped framework installed on the base supporting the rack and cylinder block, the entire base, A-shaped frame and the cylinder block assembly with through bolts together to form a rigid structure. In order to withstand horizontal crankshaft bending load, the main bearing cap fixed by the strut bolts. This enhanced structure is necessary to withstand the fire load on the diesel engine structure reached by the cylinder head. The crankshaft is a semi-modular, the crank arm is designed as part
电喷柴油机发动机工作原理和系统技术介绍48_柴油机工作原理
of the quality of balance rotation. The cylinder head was made of monomer, and equipped with a central injector, starting air valve, safety valve and indicator valve.
The constant pressure exhaust-driven turbocharger to provide scavenging air. The reflux sweep gas and auxiliary blower with an electric run automatically, so that low and maneuvered.
Lubricants for low and medium voltage systems, low pressure system to the main bearings and other bearing oil supply, the crosshead bearing the Chinese and oil of the pressure system, the hinge tube to oil sent to the crosshead bearing.
Cylinder, cylinder head and piston cooling by water, the boom of water into the piston.
The fuel injection using independent injection system, and Woodward hydraulic governor governor.
RL type of diesel engine based on the RND-M type, the piston stroke lengthened to provide greater output power and lower speed. Its new features include single-walled base with a thrust bearing, piston head and the main combustion chamber components drill air cooling, and water in the air circulation close to the hot surface of the drill.
BSULZER the RTA-type diesel engine
The SULZER RTA84C is a typical low-speed two-stroke crosshead long journey of modern diesel engines. Its bore 840mm, stroke 2400mm, speed 100r/min, 4 to 12 cylinder products can also be particularly large fast container ship production. Its design and structure and RTA2 series RTA2 series cylinder size down to 380mm. The docking station is composed of single-wall deep wall box structure welded plates and castings, welding a solid A-shaped rack is equipped with cooling liner, formed by the bolt fused cylinder. Of these parts diesel robust overall framework. The entire frame structure through bolts vertical preload.
Liner for a cast iron alloy. Its upper end is a solid ring units, located in the cylinder body, it is under a lot of gas load. The liner drilling air cooling, adjustable water flow to maintain the proper temperature. Liner the lower end of the sweep gas tank without cooling. Different height of the cylinder lubrication to reduce cylinder wear rate.
Cylinder head is solid forged steel, drilling cooling to reduce thermal stress, and pass the heat of the fuel injector, so concentrated cooling the exhaust valve seat cylinder head cooling water. For exhaust valve made of 84 # nickel-chromium titanium (Ninonic80,), and through the leaves on the stem rotation. He opened hydraulically and closed by air spring action, open the liquid pressure from the cam-driven control mechanism.
Piston with alloy steel piston head, and five compression ring installed in the ring slot chrome piston with a short cast iron piston skirt. Piston oil cooling, shock cooling and small nozzle injection, into the oil through close to the underside of the piston head and the back of the hole in the piston ring groove. Cooling oil drilling in the piston rod from the crosshead of the hinge rod for entry and return. The piston rod and monomer cross head is connected to the surface, and continuously throughout the lower half and the top bearing. The upper bearing material for the white metal by pressure oil lubrication. The crosshead oriented slider connected to each end of the crosshead.
The semi-assembly crankshaft crank to increase main bearing area recessed in the chamfer, the main bearing cap fixed by the strut bolts installed in the rack. Camshaft gear drive, with a server to run in the reverse to the fuel pump and starting air distributor retiming.
The high pressure pump is a cam-driven valve pumps, with variable ignition timing adjustment to maintain slow and efficient combustion. Mounted on the cylinder head on each high-pressure pump to the symmetrical arrangement of three injector cooling oil. In the fuel injector fuel injector the heat cycle.
This diesel engine using a DC sweep gas at constant pressure booster, with efficient cooling of the turbine turbocharger, supplemented by two high-speed electric auxiliary fan at low speed.
Diesel engine structure (II)
First, the piston and piston rod
The piston head and piston made by the lower part of a cast iron piston skirt and the upper part of a heat-resistant steel. Them together with bolts and fixed on the piston rod. Piston parts between the location of the groove of the piston head turning and positioning pin fixed.
Each piston is equipped with six piston rings, piston ring mounted on the head chrome ring slot. 3 of the top piston ring is a narrow ring with oblique incision; immediately go on the two piston rings with overlapping ride the mouth of
the wide ring, that ring in the bottom of the oil scraper ring. All piston rings top and bottom of the outer edge of a slight chamfer to left in the liner of the new piston ring running during the film.
In order to control the thermal stress, some of the modern diesel engine using thin-walled central cooling piston. In this case, a plug-in within the piston head, used for the cooling flow oriented to enhance the traditional "chicken tail shock effect.
The piston rod from the top flange to the relative position of the crosshead center boring. A long tube from the hole into the near-bottom of the hole. Tube outer diameter smaller than the diameter of the hole, so to form an annular space between the piston rod and tube.
The bottom of the piston rod diameter decreases, insert in the hole within the crosshead and the crosshead and piston rod fastening nuts. The piston rod is equipped with a locating pin to ensure that the correct assembly of the various components.
At the journal of the crosshead at both ends, each equipped with a crosshead slider. Crosshead slider inside the engine frame crosshead guides-oriented. Crosshead slider is determined by the positioning pin in the location of the cross head, cone head bolt secured to the cross head.
三 : 柴油发电机的工作原理为以柴油机带动发电机发电。某柴油发电机说明书的部分内容如下表所示。
四 : 柴油发电机工作原理
柴油发电机组的基本工作原理是依靠柴油发动机驱动发电机运转,将柴油的化学转化为电能。
柴油发电机组它以柴油为燃料,在汽缸内经过空气滤清器过滤后的洁净空气与喷油器喷射的高压雾状柴油充分混合,温度迅速升高。当达到柴油的燃点时,柴油被点燃,混合气体剧烈燃烧,体体积迅速膨胀,推动活塞下行,称为做功,由于柴油发动机有多个汽缸,各汽缸按一定的顺序依次做功,作用在活塞上的推力经过连杆变成了推动曲轴转动的力量,带动曲轴不停转动。
与柴油发动机相匹配的同步交流发电机与柴油发动机组曲轴同轴安装,柴油发电机组曲轴的转动就带动发电机转子转动。利用“电磁感应”原理,发电机就会输出感应电动势,经闭合的负载电路就能产生电流。
以上为柴油发电机最基本的发电原理。在发电过程中,还需要一系列的控制,保护器和电路,才能输出最稳定,可以使用的电力。
同步发电机的基本工作原理包含以下一个方面。
1.磁场的建立。发电机运行时,励磁绕组通过直流励磁电流,建立极性相同的励磁磁场,即建立起主磁场。
2.切割运动。原动机,柴油发电机组或汽油发电机组拖动转子旋转,机型形同的励磁磁场随轴一起旋转并顺次切割定子各相绕组的过程。
3.载流导体发电机运行后,三相对称的电流组充当功率绕组,称为感应电动势或者感应电流的载体。
4.交变电动势的产生
同步发电机的工作原理是实际上就是电磁感应原理。通过转子磁场和定子绕组的相对运动,将机械能转变为电能。当转子在原动机的带动下,转子磁场和定子导体做相对运动,即导体切割磁路线,因此在导体中产生感应电动势,其方向可根据u右手定则判断。由于转子磁极的位置是导体以垂直方向切割磁力线。所以此时定子绕组中的感应电动势最大,当磁极转动90度时,磁极成水平位置,导体不切割磁力线,器感应电动势为零。转子在转90度,定子绕组感应电动势又以垂直方向切割磁力线,使感应电动势达到最大值,但方向与前相反。当转子再转90度。感应电动势又为零。这样转子转动一周,定子绕组的感应电动势也发生正,负变化。如果转子连续均匀旋转,在定子绕组中就会感应出一个周期性不断变化的交流电动势,通过引出线,即可输出交流电流。
起动和运行操作
(1)对于停机超过24h的机组,须先打开试动阀,并起动机油泵。对于停机超过7天的机组,应测量励磁机及操作电路的绝缘电阻,必须符合要求。用手动盘车(指关闭原动机,使用手动轮转动发电机的情况)转动数圈,自由起动电机拖动柴油发动机空转数圈,以排出缸内的油和水,然后关闭试动阀,合上前离合器。
(2)起动燃油泵,放出管路中的空气,观察电压是否在规定的范围内。若正常,方可进行正式起动。
(3)察看起动电源的电压是否符合要求。若电压正常,按下起动按钮等柴油发动机正常运行后即松开。
(4)当柴油发动机运转后,观察机油压力表的指示值,当升到规定值以上时,停止机油泵,并关闭扫气泵排污阀,穿好前离合器螺钉。
(5)当发电机起动后,即认为发电机及全部电气设备均已带电,人体不得接触带电部位。
(6)发电机起动后,应逐渐提高柴油发动机的转速,并进行送电前的检查。
(7)逐渐调整柴油发动机的转速,但在调整时应注意观察发电机运转是否正常。正常时,集电环及换向器上的电刷应无跳动、无冒火花现象、无异常响声。
(8)调整发电机输出的电压和频率,其电压值应稳定并达到380v+-10v,频率应达到50Hz+-0.5Hz。
(9)当接到准备并列的信号后,应以同步表为准,进一步调整转速,调节励磁,并按以下步骤进行同步操作:
合上发电机出线的刀开关;
对于三相四线制供电的发电机,应合上中性点接地刀开关;
合上同步指示开关,检验相序,进一步调节;
认真观察同步指示器信号,当基本达到同步时,立即合上主开关,向系统送电。
注意:若发现同步表跳动或不动,同步指示灯无规则闪烁或亮度不变,则不能进行合阀。
(10)送电期间操作人员不得擅离岗位,并认真作好发电机的运行记录。
(11)送电期间,若出现柴油发动机发出异常响声、连续冒烟、频率明显下降且不能回升、电流表指针超出其额定值等情况,应立即断开送电开关,降低柴油发动机转速,停止供电。
最后还要注重柴油发电机组的日常保养和维护

五 : 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理
柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理
柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理
柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理
柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理
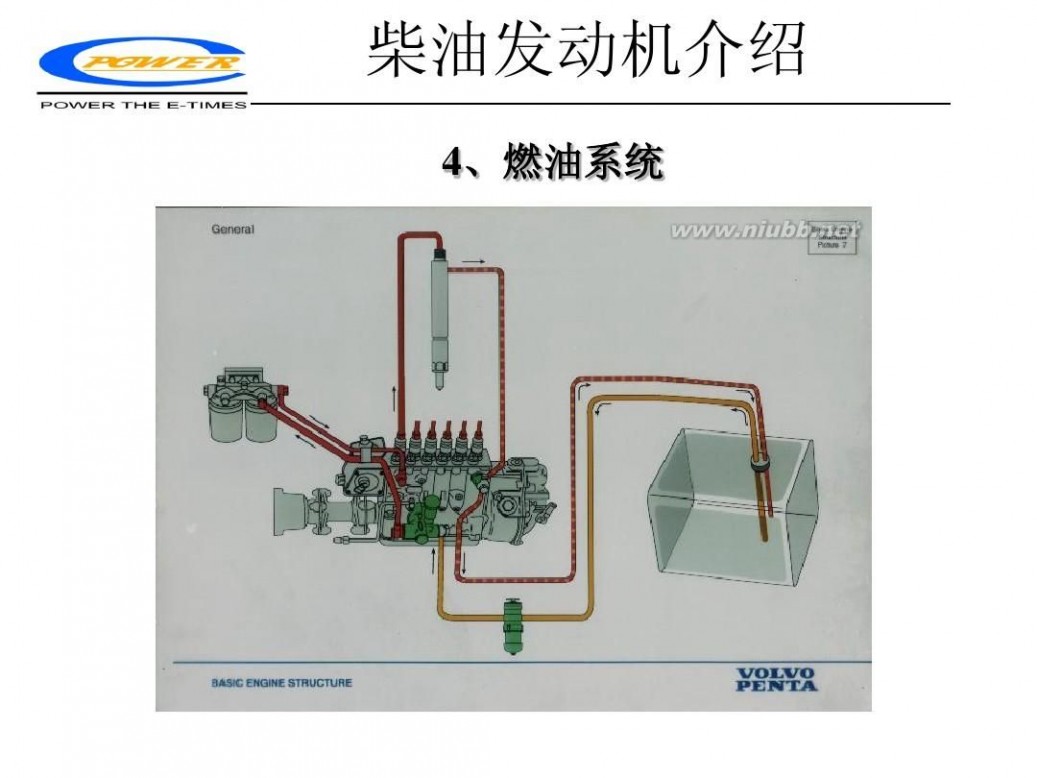
柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理
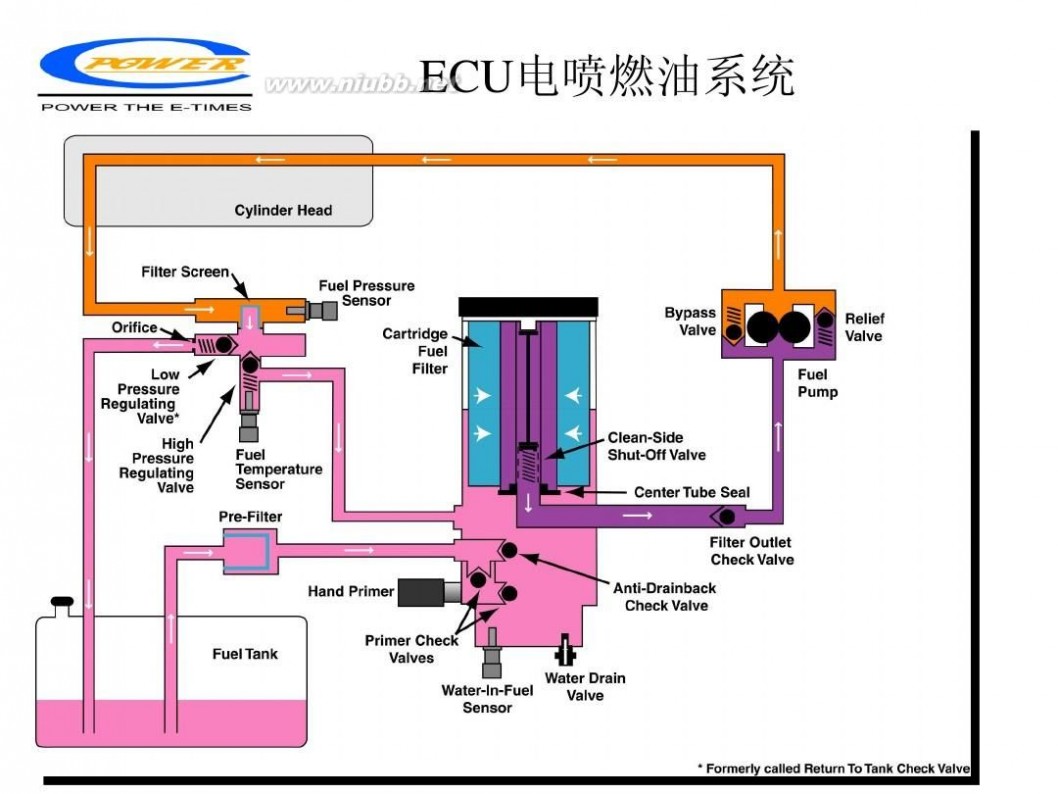
柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理
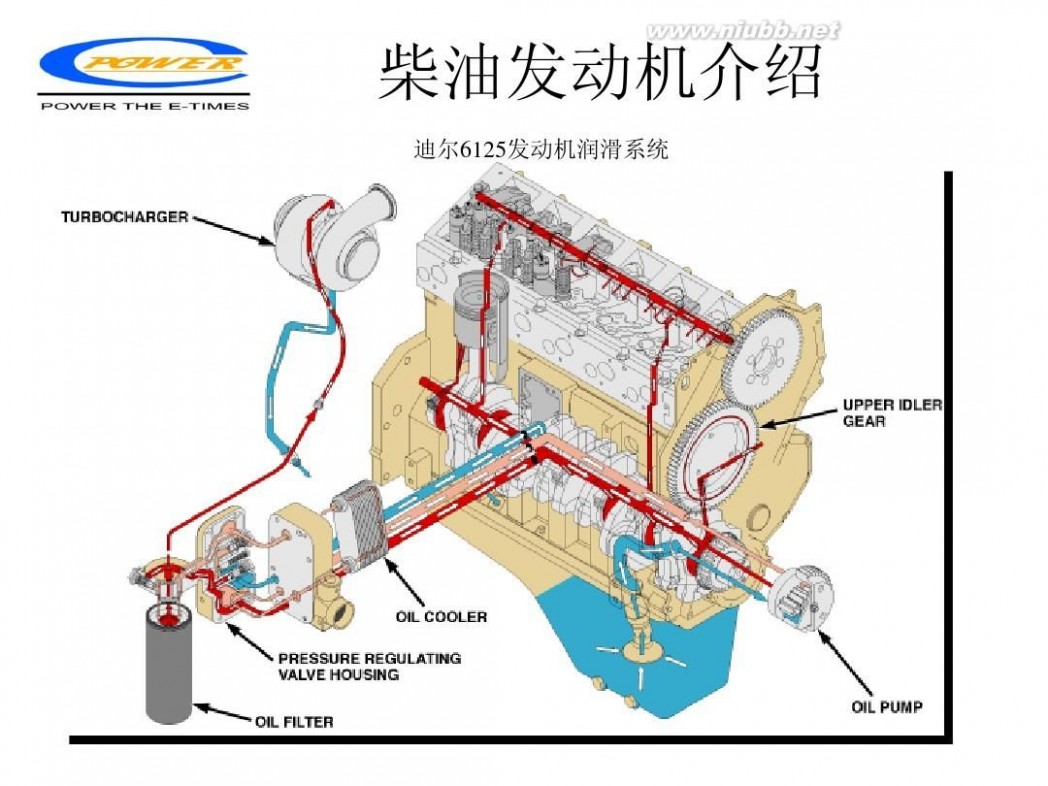
柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理
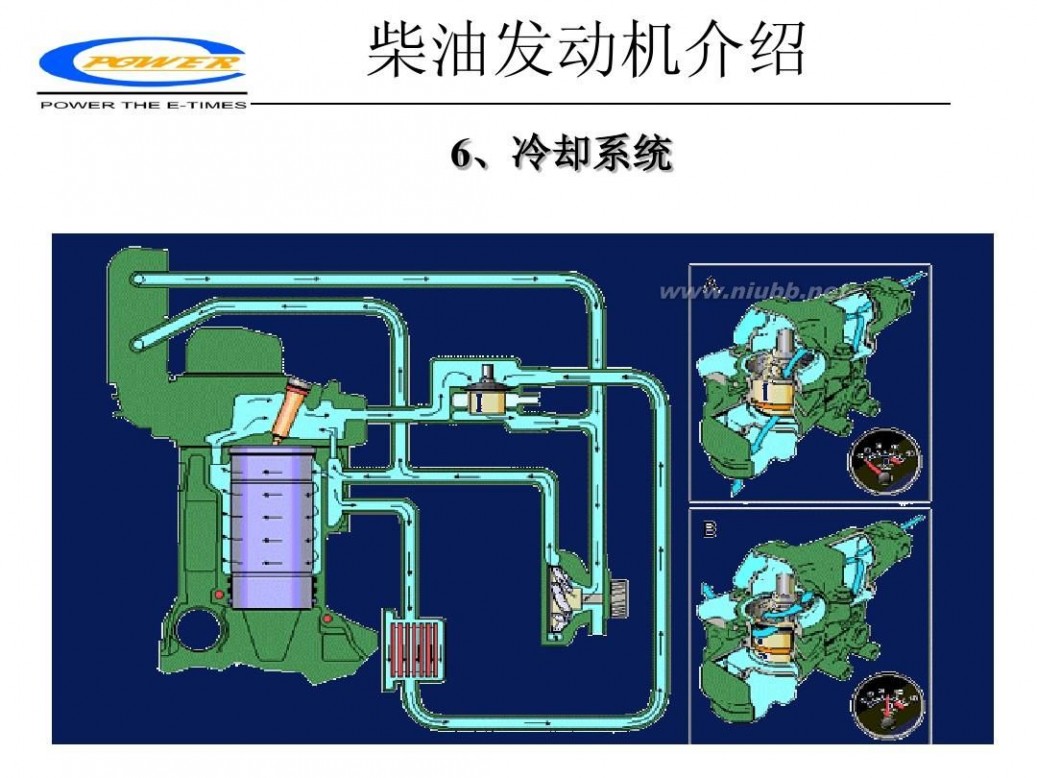
柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理
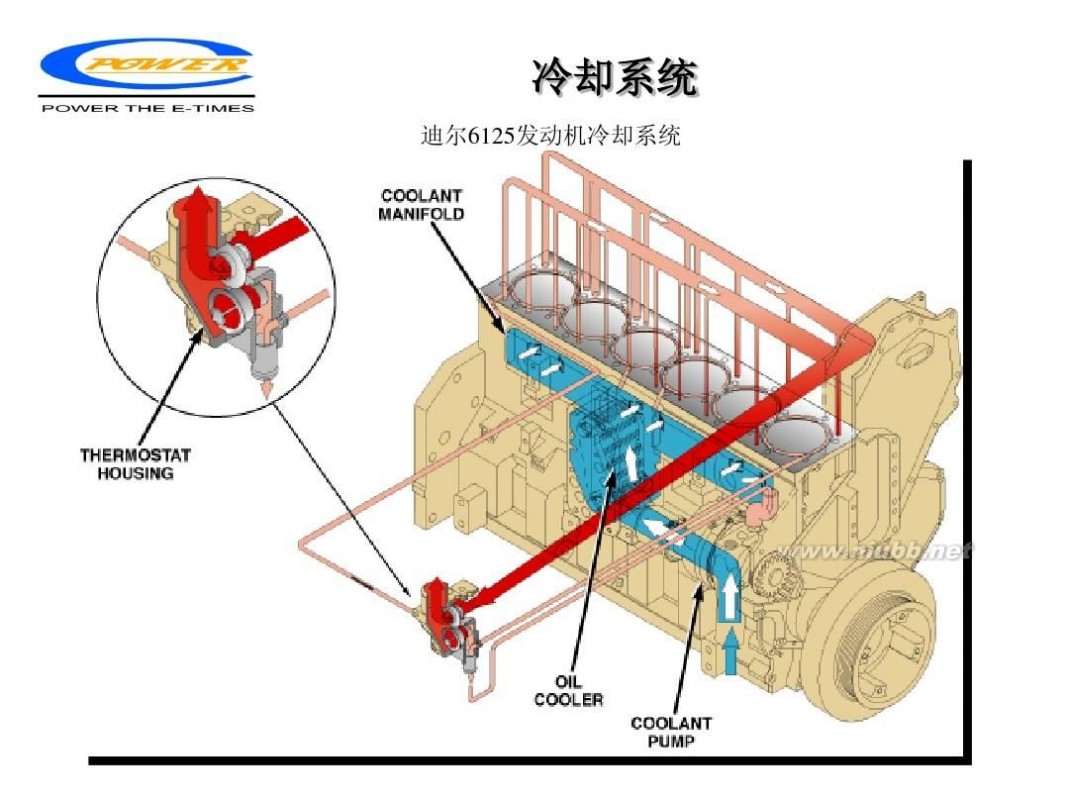
柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

柴油发动机 柴油发动机工作原理

 本文标题:柴油发电机工作原理-柴油发电机工作原理的维修保养
本文标题:柴油发电机工作原理-柴油发电机工作原理的维修保养 61阅读| 精彩专题| 最新文章| 热门文章| 苏ICP备13036349号-1